If production is too fast or too slow for the rest of your supply chain, it creates costly bottlenecks that reduce the profitability of your entire operation.
To fine-tune a production line, you need precise metrics, including:
- Takt time,
- Cycle time, and
- Lead time.
We’ll explain what each metric measures, how they relate to one another, and provide simple ways to calculate them.
Let’s dive in.

What is takt time?
Takt time is the maximum time you can spend making one unit to meet customer demand.
Originally, the German aircraft industry of the late 1930s used this metric for production scheduling. The German word “takt” means “beat” or “rhythm” — and takt time indicates your optimal production rhythm.
Interestingly, Japanese engineers from Toyota later adopted the term. When Western management theories popularized the Toyota Production System in the 1990s, takt time became a staple of the widely used lean manufacturing method.
Let’s see an example of takt time: Say you’re running a car factory, and you get 60 new car orders from customers daily. If your workers spend 360 minutes on production each day, you have 6 minutes to produce 1 unit — and that’s your takt time.
If output is slower than your takt time, you create shortages and delays. This leaves an unfulfilled demand that your competitors might exploit. On the other hand, overproduction ties up your money and builds excess inventory, resulting in higher manufacturing costs.
So, why is knowing your takt time important?
In short, it’s a key performance indicator that shows if your production meets realistic customer demand. Studies show that tracking takt time can help optimize various business processes, such as reducing mean delivery time for manufactured goods.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Want to learn more about key performance indicators? Check out our complete guide to KPIs in different industries:
Optimize production with Clockify
How to calculate takt time
Here’s the formula for takt time calculation:
Takt Time = Net Production Time / Customer Demand
Remember our car factory example from above? In that scenario, the calculation is:
360 minutes of production time / 60 daily car orders = 6 minutes per unit
Essentially, you need 2 other metrics to calculate takt time:
- Customer Demand — the number of units customers want in a set period, usually a day, and
- Net Production Time (NPT) — the time your team spends on production.
Note that NPT is only the actual time you spend on production, not the total length of a shift. So, we exclude non-production tasks from our count.
For instance, if the total shift is 480 minutes, and other tasks (like breaks, maintenance, and meetings) take 120 minutes each day — we subtract them to reach an NPT of 360 minutes.
How to get reliable NPT data
In real life, getting reliable NPT data is hard because manufacturing processes are more complex. The fastest way is to use a reliable time tracker like Clockify by CAKE.com to track only clean production time directly.
With the time clock kiosk, you can automatically track your employees’ work time spent on production, without breaks and other tasks — like below.
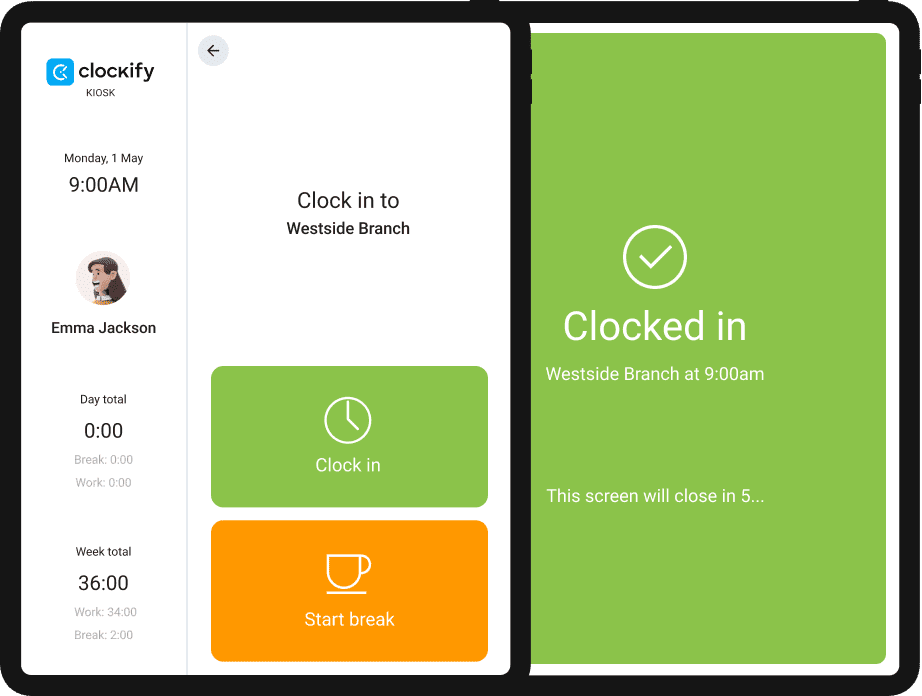
When your employees start working or take a break, they just click the appropriate button. Clockify automatically fills their timesheets, logging what everyone worked on each day — and for how long.
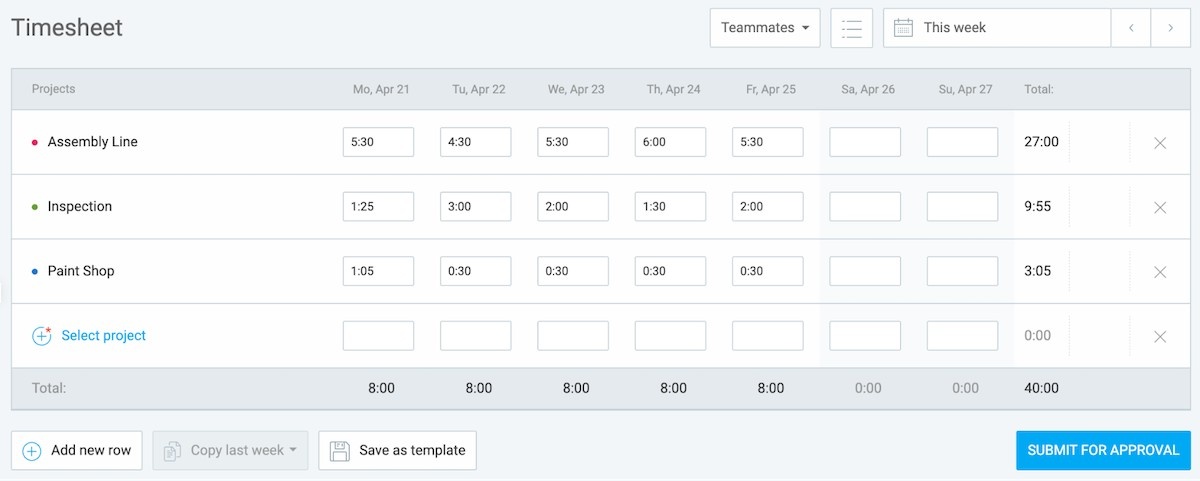
With real-time NPT data from accurate timesheets, you can calculate takt time with far greater precision.
Track production time in Clockify
Takt time calculator in Excel and Google Sheets
To calculate your takt time, use this simple takt time formula in Excel or Google Sheets:
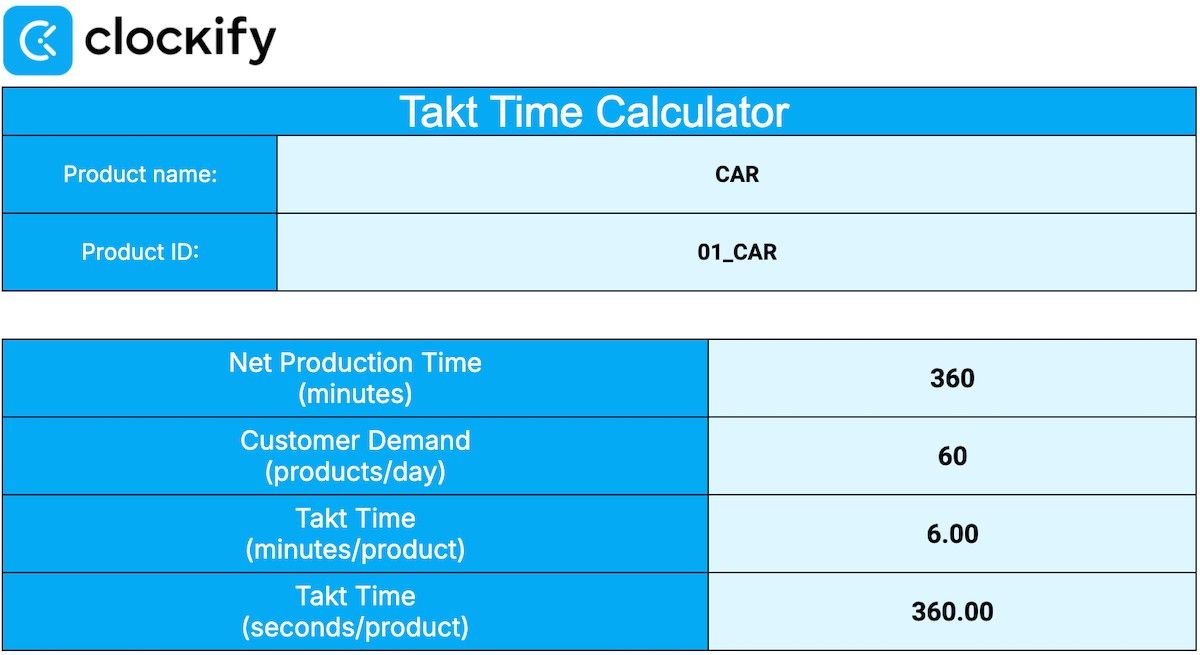
🔽 Download Takt Time Calculator in Excel
🔽 Download Takt Time Calculator in Google Sheets
What is cycle time?
Cycle time is the actual time required to produce one unit of a product from start to finish.
Let’s revisit our car factory example. You know your takt time is 6 minutes per car, and that’s the ideal speed you’re aiming for. But how quickly are your workers actually assembling cars?
If they assemble 40 units during the 360 minutes of daily production, they need roughly 9 minutes for each car. This is your cycle time.
So, cycle time shows how fast your staff is working in practice. On the other hand, takt time indicates the optimal pace at which they should work for maximum production.
For illustration, tracking cycle time helps you:
- Measure production process efficiency,
- Spot bottlenecks, and
- Compare actual production time per unit to takt time, which is your ideal target.
If your cycle time process is longer than your takt time, you’re falling behind demand. If it’s shorter, you might be overproducing.
Manufacturing companies strive for shorter cycle times to reduce the cost base of a product and enhance productivity. When cycle time is too long, it increases production costs while reducing speed.
Business owner Amra Beganovich monitors cycle time and other manufacturing metrics at her company, Colorful Socks. Tracking these metrics helps Amra maintain an efficient supply chain:

“Maintaining lead time, takt time, and cycle time allows us to see delays early. In our case, design approvals were hampering the factory’s backlog. After we clamped down on our approval process, we saved weeks at peak levels of production during the busy seasons.”
How to calculate cycle time?
Here’s how you calculate cycle time:
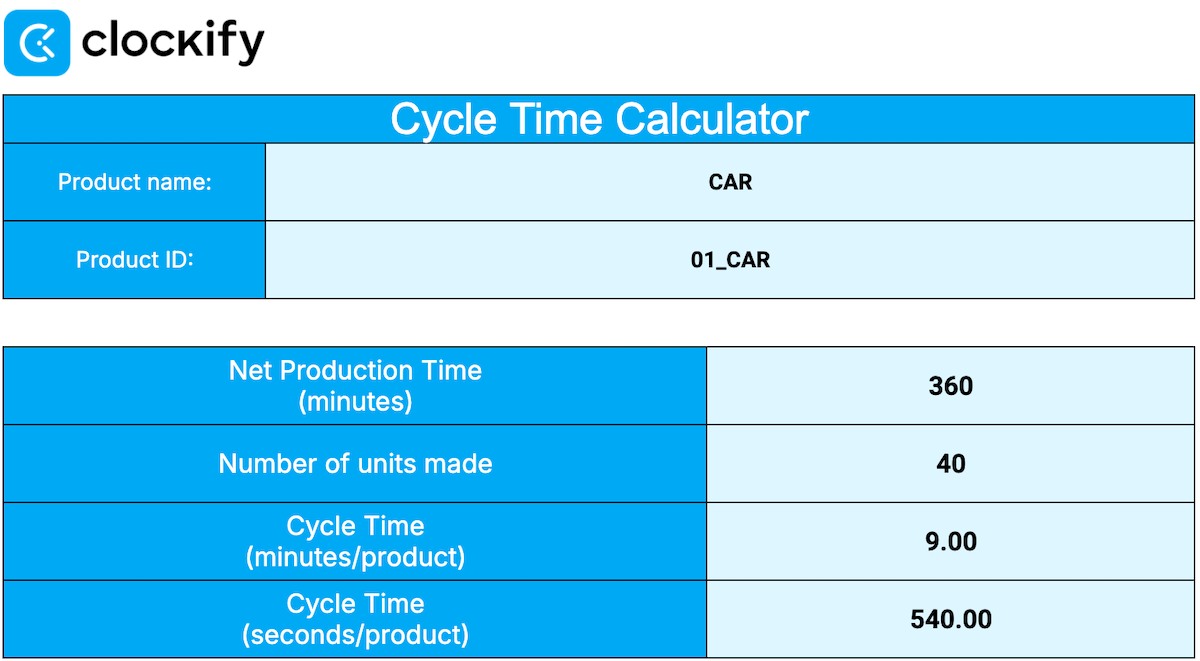
Cycle Time = Net Production Time / Number of Units made
In our example above, workers make 40 cars during their daily NPT of 360 minutes. In that case, your cycle time is:
360 / 40 = 9 minutes per unit
Since your takt time is 6 minutes, you’re lagging. Perhaps your workers wait too long for certain parts to arrive at their workstations or spend excessive time preparing the finished car for shipment. Either way, there’s room for improvement.
To reduce cycle time in manufacturing, you’ll need reliable NPT data that shows how much time your workers spend on each task. Then, you’ll know specifically where to look for inefficiencies. For example, you can use a manufacturing time clock to get precise information.
Cycle time calculator in Excel and Google Sheets
You can quickly measure your cycle time with this easy calculator:
🔽 Download Cycle Time Calculator in Excel
🔽 Download Cycle Time Calculator in Google Sheets
How to sync cycle time and takt time
To meet customer demand, you must align your cycle time with your ideal takt time. In the process, you may need to change your workflow to improve efficiency. Naturally, the hard part is doing that without sacrificing quality.
So, start by measuring your actual production time with Clockify. Then, consider using time management and productivity techniques to make improvements. Finally, break down each task and see where the delays are happening.
If your team regularly loses time to non-production tasks, consider where you can make adjustments to optimize productivity. For example, if daily meetings last 50 minutes, try shortening them to 25 and use the saved time to boost output.
Sometimes, this still won’t be enough to meet takt targets. In that case, consider hiring additional workers to increase productivity and synchronize cycle time with takt time.
To get accurate, real-time data, use a powerful tool like Clockify by CAKE.com to track cycle time for each task. Based on your workers’ timesheets, Clockify automatically creates visual reports in real time — showing you how much time different projects or tasks take.
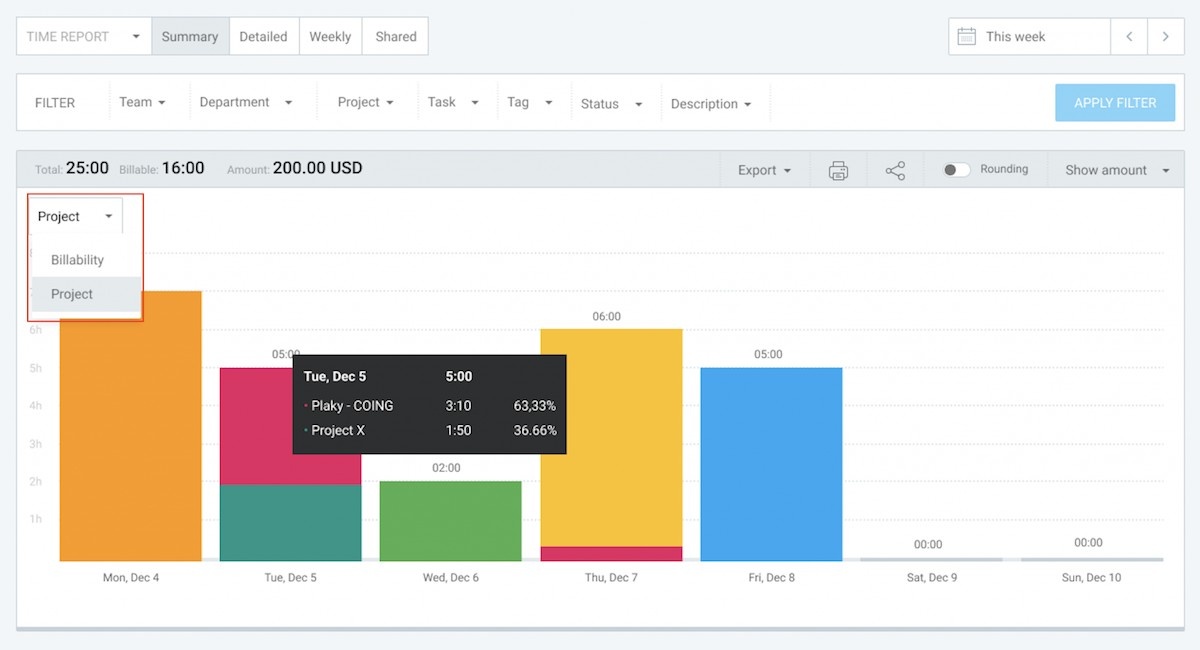
If your lead times and cycle times are too long due to lengthy breaks or an unnecessary focus on non-production tasks, you’ll quickly see this in the summary report.
As a result, you’ll be able to eliminate waste and rebalance workloads to match your ideal takt time.
Find inefficiencies with Clockify
What is lead time?
Lead time is the total time it takes to complete a process from start to finish.
In our car factory scenario, this metric measures the time from the moment a customer places an order to the moment they receive their vehicle. Besides the manufacturing process, this lead time includes pre-production tasks and delivery.
Depending on your sector, lead time can mean different things, such as:
- Manufacturing — the time between getting a production request and producing the required goods,
- Supply chain management — the time between placing an order with a supplier and receiving the requested items, and
- Project management — the time between a project’s start and end date, or the time between the end of one task and the beginning of another.
Lead time is more closely tied to cycle time and takt time in manufacturing, so we’ll cover this in detail below.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Struggling to create a work schedule that keeps lead times short and your workers satisfied? Check out our guide to arranging shifts optimally:
How to calculate lead time?
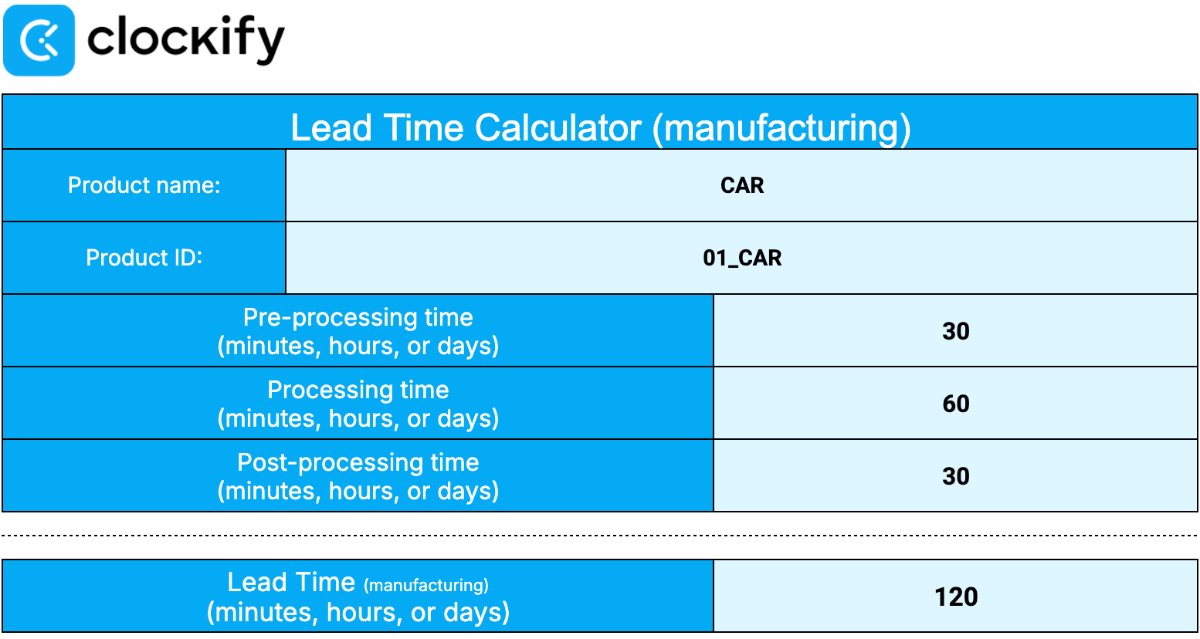
Here’s how lead time is calculated in manufacturing:
Lead Time (Manufacturing) = Pre-processing Time + Processing Time + Post-processing Time
As you can see, we measure lead time by adding up the time spent in all stages of production.
Without concrete data on lead times, companies have unpredictable inventory management. This can lead to both increased carrying costs and sudden shortages of goods.
Here’s how business owner Amra Beganovich dealt with long lead times at her company:

“Long lead times tend to happen due to missing materials, lack of approval, or delays. To reduce lead times, we collaborated with vendors more closely on forecasting orders and made strict internal deadlines based on the production schedule. Clear communication and establishing small buffer windows for each link kept everything flowing without inflating costs.”
To find bottlenecks and improve efficiency at every step, you can further break down each stage of lead time into:
- Order Lead Time — Time from receiving a customer order to delivering the final product,
- Order Handling Lead Time — Time from receiving the customer order to creating an official sales order,
- Manufacturing Lead Time — Time from the sales order to the end of production,
- Production Lead Time — Time from the start of physical production to the end of production, and
- Delivery Lead Time — Time from finished production to customer delivery.
Note that some of these lead times overlap. For example, order lead time includes all stages of production, from order receipt to delivery.
In Clockify, timesheets automatically calculate the lead time for each day of production.
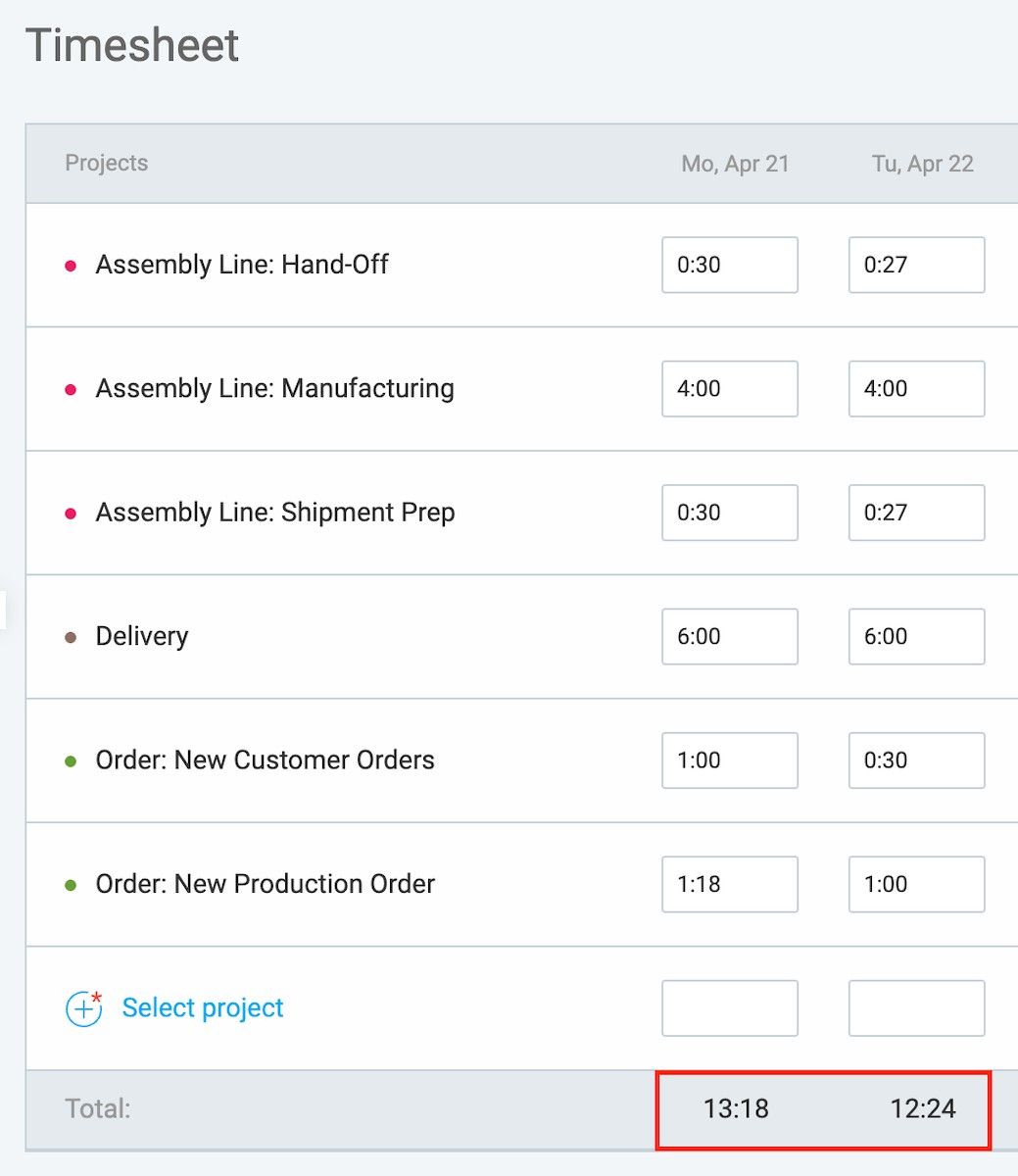
If you track all tasks with Clockify, you can see the daily time spent on them at the bottom of the timesheets.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Want to maximize performance and output? Learn more about productivity and efficiency in our detailed guide:
Lead time calculator in Excel and Google Sheets
To learn how long your customers usually wait from the moment they order a product, you can use this handy calculator and learn your total lead time:
🔽 Download Lead Time Calculator in Excel
🔽 Download Lead Time Calculator in Google Sheets
Takt time vs cycle time vs lead time
All 3 key manufacturing metrics provide vital insights into your production rate. Here’s a quick overview of how we use each one:
| Manufacturing metric | What it tells you | Your main goal |
|---|---|---|
| Takt time | How fast you should produce | Align with the actual demand for ideal production |
| Cycle time | How fast you produce each unit in practice | Optimize for efficiency |
| Lead time | How long customer wait for your product | Reduce to increase customer satisfaction |
To get an overview of all 3 metrics in one place, here’s a combined calculator that helps you measure each one:
🔽 Download Takt Time + Cycle Time + Lead Time Calculator in Excel
🔽 Download Takt Time + Cycle Time + Lead Time Calculator in Google Sheets
Optimize your production with Clockify by CAKE.com
In practice, modern manufacturing is a complex process that requires continuous improvement.
Calculating manufacturing metrics becomes harder if your company produces multiple products, each with its own production times and varying customer demand.
As a feature-rich project time tracker, Clockify helps you track metrics for multiple products simultaneously — see below.
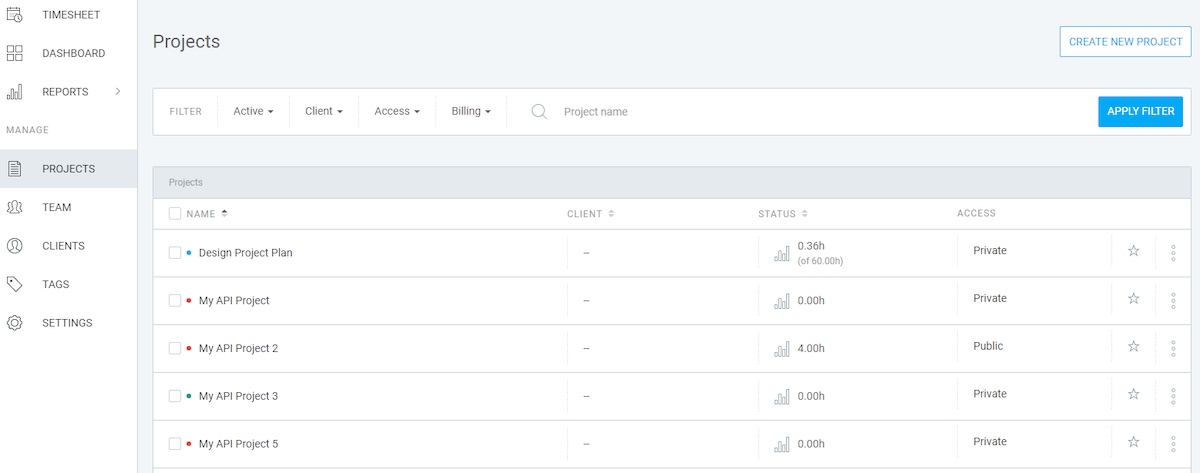
For instance, you can create separate projects for each product and track their metrics individually. This helps you identify inefficiencies and make adjustments on time, avoiding long lead times and low customer satisfaction.
You can also use Clockify’s forecasting function to predict takt time and see if your cycle time and lead time meet expectations.
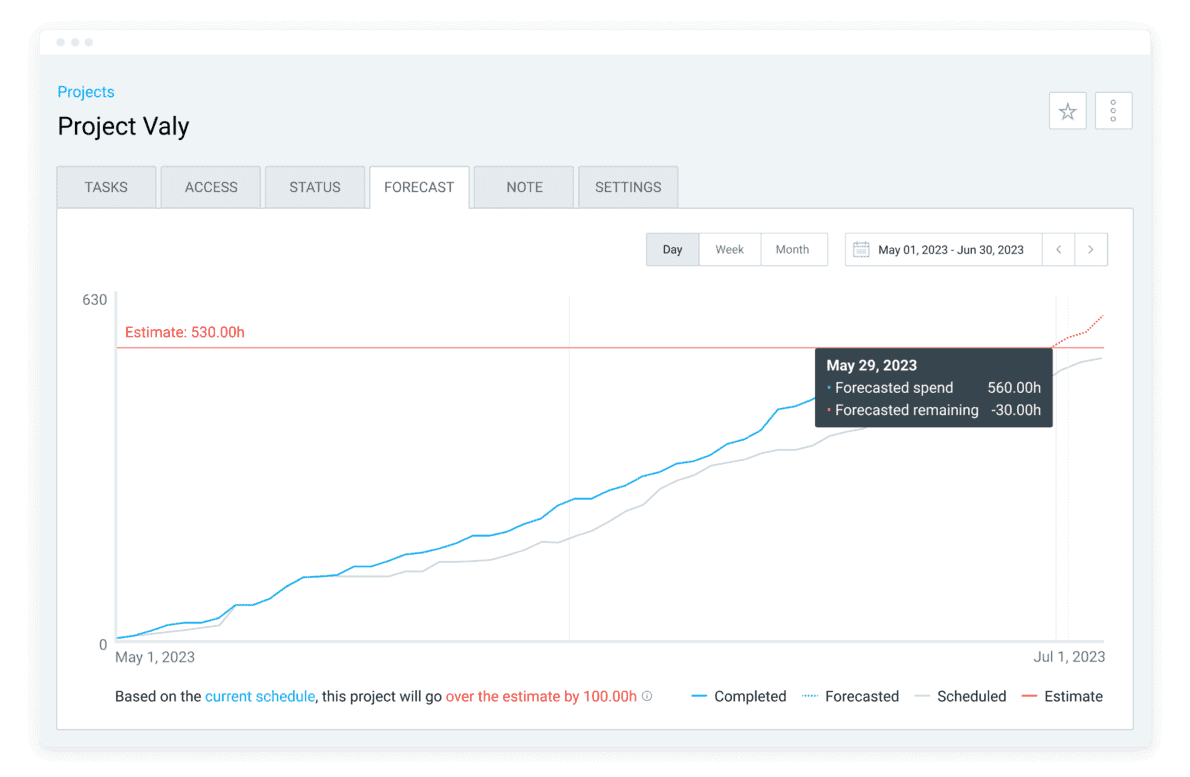
If you haven’t used similar software before, don’t worry — you don’t need any experience with time tracking software to use Clockify’s simple yet powerful features. You only need a few minutes for the initial setup on any device.
And if you have any questions, every user gets 24/7 support via chat, email, or phone — regardless of their subscription tier.
Use Clockify by CAKE.com to remove bottlenecks before they cause delays and additional costs.