Kansas Labor Laws Guide
Ultimate Kansas labor law guide: minimum wage, overtime, break, leave, hiring, termination, and miscellaneous labor laws.
| Kansas Labor Laws FAQ | |
| Kansas minimum wage | $7.25 |
| Kansas overtime | 1.5 times the regular wage for any time worked over 46 or 40 hours/week ($10.87 for minimum wage workers) |
| Kansas breaks | Breaks not required by law |

Wage laws in Kansas
Kansas is one of the many US states that completely adheres to federal regulations. In other words, there are no state laws regulating wages, and therefore, the federal rules apply.
The following are wage regulations concerning the state minimum wage, the tipped hourly wage, and the youth minimum wage in Kansas.
| KANSAS MINIMUM WAGE | ||
| Regular minimum wage | Tipped minimum wage | Subminimum wage |
| $7.25 | $2.13 | $4.25 |
Minimum wage in Kansas
As of January 1, 2010, Kansas employers are obligated to pay their employees the federal minimum wage of at least $7.25 per hour.
Tipped minimum wage in Kansas in 2025
Tipped employees in Kansas are entitled to the federal tipped minimum wage, which is $2.13 per hour.
However, the total earnings of a tipped employee (hourly tipped minimum wage + tips) must be at least $7.25 per hour. If a tipped employee doesn’t make $7.25 per hour, the employer is obliged to make up the difference.
Subminimum wage in Kansas in 2025
Under federal law, employers can pay certain types of employees a lower minimum wage — known as the subminimum wage.
Employees eligible for subminimum wages include:
- Youth workers for the first 90 days of their employment,
- Full-time students, and
- Workers with disabilities.
Employers who wish to employ an individual under 20 can pay them $4.25 per hour for the first 90 calendar days of employment.
Furthermore, full-time students who work in retail, agriculture, colleges, or universities can be paid 85% of the minimum wage — that is, $6.16 per hour. Employers who employ full-time students must obtain a certificate from the US Department of Labor.
When full-time students graduate or leave school for good, they’re entitled to the federal minimum wage of $7.25 per hour.
Employers can also obtain a certificate from the Wage and Hour Division, which allows them to pay a special wage lower than the federal minimum to workers with disabilities.
Exemptions to the minimum wage in Kansas
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) states that certain employees are exempt from the minimum wage.
The following is the list of some exempt employees (together with specific requirements):
- Executive workers who are paid on a salary basis and earn not less than $1,128 per week,
- Administrative workers who are paid on a salary basis and earn not less than $1,128 per week,
- Learned and creative professionals paid on a salary basis who earn not less than $1,128 per week,
- Highly compensated employees who earn $151,164 or more a year,
- Outside sales employees — no minimum salary requirement,
- Employees with disabilities,
- Babysitters,
- Tipped employees, and
- Minors.
Payment laws in Kansas
Employers in Kansas are obligated to pay all wages due to their employees at least once in a calendar month or as agreed upon by the employer and employee.
Other most common payment frequencies in the US include the following:
- Weekly — employees are paid once a week (52 paychecks per year),
- Bi-weekly — employees are paid every other week (26 paychecks per year), and
- Semi-monthly — employees are paid twice per month (24 paychecks per year).
🎓 Guide to Pay Periods: How Many Pay Periods in a Year & How to Choose the Best One
Overtime laws in Kansas
Under federal law, covered non-exempt employees are entitled to overtime premium pay of at least 1.5 times the regular pay rate.
While federal law proposes that overtime work is any hour worked over 40 hours within a week (except for weekends or holidays), the state law of Kansas says otherwise. Under state law, however, employees in Kansas must work more than 46 hours per week to be eligible for overtime pay of 1.5 times the regular rate.
Factors that determine whether federal or state law applies to an employee’s overtime rate involve the amount of annual revenue and interstate commerce of a business.
To find out whether you fall under federal or state overtime regulations, contact the Federal Wage and Hour Division.
Overtime exceptions and exemptions in Kansas
However, some employees don’t have to work 46 hours a week to be eligible for overtime pay. According to the FLSA, employees engaged in commerce or the production of goods are eligible for overtime pay after 40 work hours in a week.
Moreover, the 46-hour rule doesn’t apply to:
- Any employee who is engaged in selling motor vehicles for a non-manufacturing employer,
- Any person sentenced to the custody of the Secretary of Corrections, and
- Any person serving a sentence in a county jail.
As with minimum wage exemptions, federal law also exempts specific categories of employees from overtime provisions, including:
- Executive employees who earn a salary of at least $1,128 per week,
- Administrative employees who earn a salary of at least $1,128 per week,
- Highly compensated employees who make at least $151,164 per year,
- Learned and creative professionals who receive a salary of at least $1,128 per week,
- Aircraft and boat salespeople,
- Taxi drivers,
- Computer employees who work on a salary basis and earn at least $27.63 per hour, and
- Outside sales employees.
In April 2024, the US Department of Labor announced a final rule regarding overtime and minimum wage exemptions for executive, administrative, and professional employees. Under this rule, the standard salary threshold will increase every 3 years due to rising inflation rates.
Fluctuating Workweek Method (FWW) in Kansas
Certain non-exempt salaried employees are entitled to overtime pay thanks to the Fluctuating Workweek Method (FWW). Employees must have a work schedule that varies from week to week (fluctuating workweek) to be eligible for this type of overtime pay.
For instance, a salaried, non-exempt employee will receive the same monthly salary whether they work 40 hours per week, fewer than 40, or more than 40.
However, for each hour worked over 40 a week, employees can receive an overtime premium of one-half (0.5) times their hourly rate.
Employees are eligible for the FWW method if they:
- Have a fluctuating workweek,
- Receive a fixed salary, and
- Get at least the federal minimum of $7.25 per hour.
In addition, employees who use the FWW are entitled to additional pay or benefits such as:
- Bonuses,
- Commissions, and
- Hazard pay.
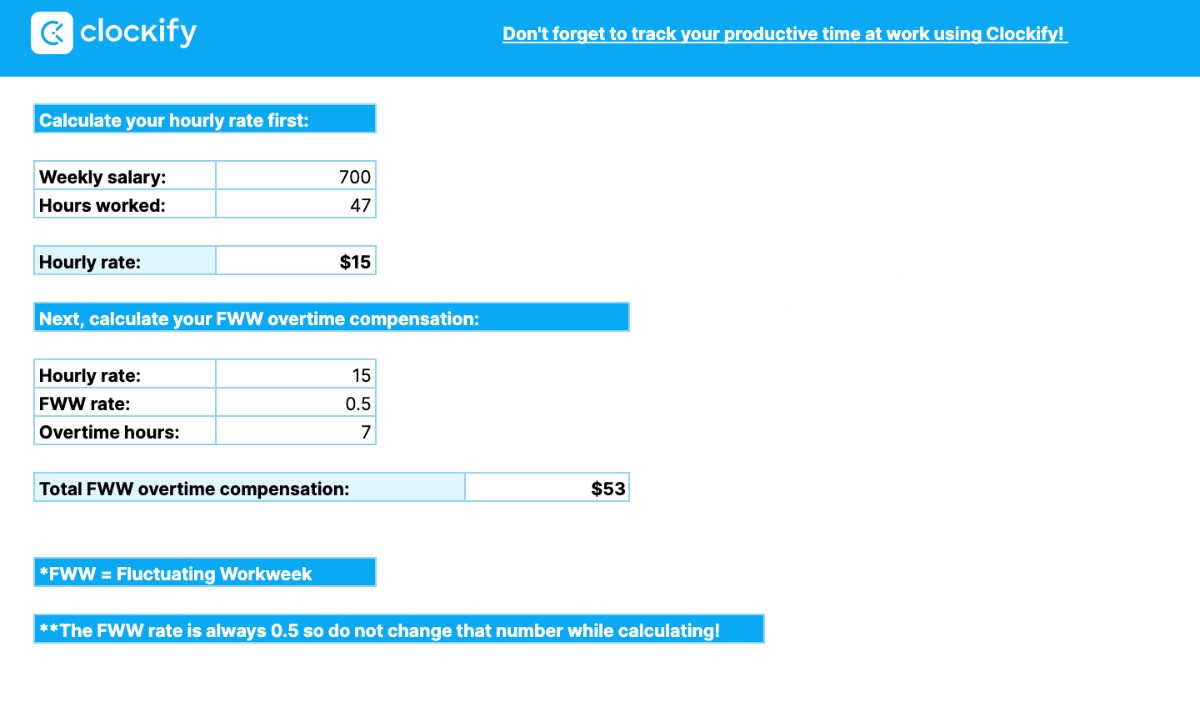
Take a look at the example of the FWW:
Let’s say an employee’s weekly income is $800, and the employee worked 43 hours in the preceding week.
To calculate overtime hours, let’s calculate the hourly rate first. Simply divide the weekly salary by the number of hours worked that week:
$800 / 43 = $19 per hour
Next, multiply the hourly rate by 0.5 for every overtime hour during a week:
$19 per hour x 0.5 = $9.5 for each overtime hour worked
Total overtime compensation goes as follows:
$9.5 x 3 overtime hours =$29
🎓 Fluctuating Workweek Calculator
Break laws in Kansas
In Kansas, neither state nor federal laws require employers to provide breaks to their employees.
However, many employers decide to provide breaks to employees to increase productivity. In that case, the following rules apply regarding break compensation:
- Short breaks — breaks that last anywhere from 5 to 20 minutes, and are considered compensable.
- Meal breaks — usually last at least 30 minutes and aren’t counted as work time, nor are they compensable.
Employees who are required to work during their meal breaks (e.g., factory workers) must be compensated for that time, as it is counted as work time.
Breastfeeding in the workplace laws in Kansas
Under state law in Kansas, breastfeeding mothers are allowed to breastfeed anywhere they have the right to be.
However, there are no state regulations regarding breastfeeding in the workplace.
In this case, the federal PUMP Act protects mothers who breastfeed in the workplace. Under the PUMP Act, employers must provide reasonable break time for breastfeeding and a private room that meets the following requirements:
- The room is shielded from view,
- The room is free from intrusion, and
- The room isn’t used as a bathroom.
Breastfeeding mothers are entitled to these protections for up to 1 year after the child’s birth.
Leave requirements in Kansas
Even though the FLSA states that an employer is not obliged to pay for time not worked, most employers do provide time off to their employees — whether paid or unpaid.
Employers in Kansas also tend to provide leave to their employees. However, public and private employees are sometimes entitled to different benefits.
In Kansas, there are 2 types of leave days:
- Required leave, and
- Non-required leave.
Let’s look at these types of leaves in more detail.
| TYPES OF LEAVES |
| ✅ REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Holiday leave (public employers) — State offices need to provide their employees with a day (or days) off for legal public holidays recognized by the state of Kansas. Legal public holidays and observances in Kansas in 2025 include:
The law doesn’t require employers to offer holiday pay, but many employers provide this benefit to their employees to help attract and retain quality employees. |
| ✅ REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Family and Medical Leave — The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) is a federal law that offers eligible employees unpaid leave of up to 12 workweeks within a consecutive 12-month period. This type of leave is used in situations such as:
To qualify for FMLA, an employee must have worked for the employer for at least 12 months and at least 1,250 hours. |
| ✅ REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Military leave (public employers) —Each state employee, whether regular or temporary, shall be granted paid military leave of up to 30 working days in each 12 months between October 1 and September 30. Eligible employees may use military leave for active or inactive military duty, full-time National Guard duty, weekend drills, or any other military duty. |
| ❌ NON-REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Vacation leave — Neither federal nor state law requires employers to offer vacation leave to their employees. Still, many employers do provide this benefit to improve employee work-life balance. |
| ✅ REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Domestic violence or sexual assault leave — Any victim of domestic violence or sexual assault may use any accrued leave or, if accrued leave is unavailable, leave without pay of up to 8 days per calendar year. |
| ✅ REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Administrative leave is a reward for an employee or a group of employees who showed amazing results outside their regular scope of work or exceeded the normal expectations. Such an employee or a group of employees may be awarded an additional 3 days off. |
| ✅ REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Donor leave (public employees) — The Kansas Donor Leave Program provides recovery time off for state employees who donate organs, blood or blood products, or bone marrow. Eligible employees may receive:
This leave can’t be used to care for family members who are donors. Moreover, donor leave will be paid at the regular rate. |
| ❌ NON-REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Sick leave — The same rules apply to sick leave in Kansas. No law obliges an employer to provide sick leave benefits to their employees, either paid or unpaid. |
| ❌ NON-REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Holiday leave (private employers) — Private employers aren’t required to provide holiday leave benefits to their employees. Moreover, they aren’t required to pay employees any premium wage rates for working during holidays. Such benefits are agreed upon by the employer and employee. |
| ✅ REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Jury duty leave — Jury duty is an obligation of each US citizen who receives an invitation from a court (i.e., summons to serve as a juror during a court proceeding). In Kansas, each regular employee must be granted paid leave for required jury duty or to be a witness before the civil service board. If the employee is called as a witness on the employee’s behalf, such an employee isn’t entitled to paid leave. |
| ✅ REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Bereavement leave (public employers) — This type of leave is granted in case of the funeral or death of the employee’s immediate family member or close relative. In Kansas, regular employees are entitled to paid leave of up to 6 working days. |
| ✅ REQUIRED LEAVE |
|
Disaster service leave (public employers) — State employees who are certified disaster service volunteers of the American Red Cross are granted a paid leave of no more than 20 working days in a 12-month period. Such employees receive compensation at their regular rate of pay. |
Child labor laws in Kansas
The child labor regulations in Kansas protect minors from any physical, moral, or emotional hazard.
Therefore, if an employer wishes to employ a minor under 16, they must obtain a work permit first.
Still, the work permit isn’t required if the minor attends any state secondary school.
Work time restrictions for Kansas minors
Under federal law, children aged 16 and 17 may be employed for an unlimited number of hours in any occupation other than those deemed hazardous by the Secretary of Labor.
On the other hand, minors under 16 have the following time restrictions (federal regulations):
- May work between 7 a.m. and 7 p.m. (except from June 1 through Labor Day, when they can work until 9 p.m.),
- May work up to 3 hours on a school day,
- May work 8 hours on a non-school day,
- May work 18 hours in a school week, and
- May work 40 hours on a non-school week.
Furthermore, Kansas law states that children under 16 who are employed in hotels, restaurants, mercantile establishments, or in transmitting merchandise or messages may work from 7 a.m. to 10 p.m., provided the following day isn’t a school day.
This group of minors can also work a maximum of 8 hours a day and up to 40 hours a week. These restrictions don’t apply to students engaged in food service preparation or vocational training programs.
When it comes to children under 14, they’re not allowed to be involved in any occupation or trade in any business or service, except in the following cases:
- If they’re employed by their parents in non-hazardous occupations,
- If they work in domestic service or casual labor in or around a private home,
- If they deliver newspapers or perform messenger duties,
- If they work in agricultural, horticultural, livestock, or dairying establishments, and
- If they’re employed as actors, actresses, or performers in movies, theaters, radio, or TV.
Finally, minors under 14 aren’t allowed to perform said services when school is in session.
Breaks for Kansas minors
Unlike other states, Kansas doesn’t regulate meal periods for minor employees.
In addition, the federal provisions for child labor don’t regulate or require breaks or meal periods for minors either.
Prohibited occupations for Kansas minors
By the Secretary of Labor, no child under 18 years of age can be employed in any occupation, trade, or business that presents any physical, moral, or emotional hazard.
Prohibited occupations for all minors under the age of 18 include:
- Manufacturing or storing explosives,
- Operating motor vehicles,
- Coal mining,
- Forest fire prevention,
- Occupations that involve working or being exposed to radioactive substances,
- Power-driven woodworking machines, and
- Wrecking, demolition, and ship-breaking operations.
Minors of any age whose parents own a business or a farm are exempt from these regulations, except for mining, manufacturing, and other occupations where the minimum age requirement is 18.
🎓 Prohibited Occupations for Non-Agricultural Employees
🎓 Prohibited Occupations for Agricultural Employees
Posting requirements for employers employing minors in Kansas
Each employer who employs minors under 16 must keep a notice in a conspicuous place stating the maximum number of hours such a minor is allowed to work.
Penalties for employers employing minors in Kansas
Any person, firm, or corporation that violates any preceding provisions will be deemed guilty of a misdemeanor and serve an imprisonment sentence of no fewer than 30 days and no more than 90 days in a county jail.
Employers will have to pay a fine of no less than $25 and no more than $100 for less severe violations.
Hiring laws in Kansas
Certain practices regarding employment in Kansas can be considered unlawful — these practices include discrimination based on:
- Age,
- Race and religion,
- Color,
- Gender,
- National origin, and
- Disability.
Unlawful employment practices in Kansas
In Kansas, certain employment practices can be viewed as unlawful. Therefore, any employer, employment agency, or labor organization isn’t allowed to:
- Refuse to hire, exclude, or expel from its membership an individual based on their race, religion, color, sex, national origin, ancestry, or disability,
- Refuse to list and properly classify for employment or to refuse to refer any potential job candidate based on their race, religion, color, etc.,
- Limit, discriminate, or deprive any person of employment opportunities because of their age (age of 40 or more years),
- Refuse to hire a prospective employee because of their height, except if the job in question is a fireman, law enforcement, or security officer, where the minimum height restriction is 5’2 (five feet two inches),
- Give preferences in hiring to relatives, friends, or neighbors,
- Exclude or deny equal jobs or benefits because of the disability of a job applicant,
- Refuse to make reasonable adjustments to adapt to the job applicant’s physical or mental limitations, provided that those limitations don’t adversely affect the business,
- Refuse to hire a job applicant because of the need to make reasonable adjustments to fit the job applicant’s needs,
- Use employment tests or other selection criteria to screen out job applicants with disabilities,
- Subject a prospective employee to any genetic screening or testing, and
- Refuse, deny, or make distinctions in offering goods, services, or facilities to any person because of race, religion, color, sex, disability, national origin, or ancestry.
However, an employer is allowed to fill vacancies in a way that reduces imbalance concerning race, religion, color, sex, disability, national origin, or ancestry.
🎓 Unlawful Discriminatory Practices in Kansas
Right to work law in Kansas
Kansas is another “right-to-work” state, meaning that employees are free to decide whether to join a labor union.
Under this law, an employee shall not be forced to join a labor union as a condition of employment. Kansas adopted a right-to-work statute in 1958.
The Kansas right-to-work amendment distinguishes:
- Schools, and
- State departments.
The right-to-work law at schools
Concerning schools, neither the board of education nor administrative employees (i.e., anyone who has the authority to hire, transfer, or lay off other employees) is allowed to:
- Discriminate while hiring based on membership or non-membership in any professional employee organization, and
- Interfere with, restrain, or force professional employees to join, form, or assist professional employee organizations.
On the other side, professional employees employed by a board of education in a professional, educational, or instructional capacity have the right to:
- Form, join, or assist professional employee organizations to establish, maintain, protect, or improve terms and conditions of professional service, and
- Refrain from any of the preceding activities.
The right-to-work law in state departments
Under this law, public employees (i.e., employees employed by a public agency except for professional employees of school districts) have the right to:
- Participate, join, or form organizations for meeting and exchanging opinions with public employers, and
- Choose to refrain from any of the preceding activities.
At the same time, public employers or their representatives are not permitted to:
- Interfere, restrain, or force public employees to form, join, or participate in employee organizations,
- Encourage or discourage membership in any employee organization, committee, association, or similar organization, and
- Discriminate or blacklist while hiring because of the membership in a said organization.
Termination laws in Kansas
Kansas is another US state that recognizes at-will employment. This employment arrangement allows an employer to fire an employee at any time for any reason — provided that it’s not based on discrimination, retaliation, or similar.
However, at-will employment works both ways. Employees may also choose to resign from their jobs at any time without any losses, penalties, etc.
Final paycheck in Kansas
In case of job loss — whether voluntary or involuntary — the employer must pay wages due to the employee on the next regular payday.
If an employer fails to give the departing employee their final paycheck in time, such employer will be required to pay a fixed amount of 1% of the unpaid wages for each day (except Sunday and legal holidays) of being late.
Health insurance continuation in Kansas
As for health coverage after a job loss in Kansas, the federal Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA) comes to aid.
COBRA is a health insurance program that allows employees and their dependents to stay on their health plans for another 18 to 36 months in the following situations:
- Employment termination,
- Reduction in work hours,
- Transitioning to another job,
- Death of a covered employee,
- Divorce, and
- Other life events.
Nonetheless, the COBRA law only covers businesses with 20 or more employees.
Occupational safety in Kansas
The Kansas Department of Labor ensures businesses and public offices provide employees with a hazard-free working environment.
Therefore, the Secretary of Labor has the right to enter any state or private office, mill, workshop, or any other place where labor is performed to ensure that safety measures are followed.
If any of the measures concerning heating, ventilation, sanitary arrangements, and similar are found to be hazardous to the health of persons working there, the Secretary of Labor then notifies the owner of such a place in writing.
Such notice may include an order that requires alterations, additions, or changes to ensure the safety of the employees.
The business owner is then required to induce changes, alterations, or additions identified by the secretary within 60 days after the notice.
Anyone who violates the provisions of this statute will be guilty of a misdemeanor or pay a fine of not less than $25 nor more than $100.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
Private employers and workers in Kansas are under the federal jurisdiction of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
OSHA was created to ensure safe and hazard-free conditions for workers. It sets safety and health standards that employers are responsible for providing to prevent work-related injuries and fatalities.
OSHA recognizes 6 main types of hazards in the workplace:
- Biological hazards — mold, pests, insects, etc.,
- Chemical and dust hazards — pesticides, asbestos, etc.,
- Work organization hazards — things that cause stress,
- Safety hazards — slips, trips, falls, etc.,
- Physical hazards — noise, radiation, temperature extremes, etc., and
- Ergonomic hazards — repetition, lifting, awkward postures, etc.
The authorities have the right to enter the premises during working hours and assign penalties for violating this act.
🎓 OSHA penalties for employers
Miscellaneous labor laws in Kansas
Some labor laws don’t belong to any specific group above, so we’ve placed them in the miscellaneous section.
The most significant miscellaneous laws in Kansas include:
- Whistleblower laws, and
- Recordkeeping laws.
Whistleblower laws in Kansas
Under the Kansas Whistleblower Act, no supervisor or representative of any state agency is allowed to prohibit a state employee from reporting any violation of state or federal regulations to any legislative person or entity.
The employee who decides to “blow the whistle” doesn’t have to notify the supervisor or appoint authority before making such a report.
If a state employee suffers any disciplinary action taken against them, such employee may file an appeal to the state civil service board within 90 days after the alleged disciplinary action.
Should the board find a violation of the whistleblower act, the violator may be suspended without pay for up to 30 days or even up to 2 years for repeated violations.
Recordkeeping laws in Kansas
As of January 1, 1978, every employer must make and keep records of each employee employed in the establishment for up to 3 years. The records must be kept in or around the premises where employees are employed.
The records of each employee should contain:
- Name,
- Occupation,
- The rate of pay,
- The amount paid on each paid period, and
- The hours worked each day and week.
What’s more, employers covered by the FLSA must keep and maintain the following records:
- Name, address, date of birth (if younger than 19), and sex,
- Occupation,
- Hours worked each day and week,
- The exact time and day of the week when the employee’s workweek begins,
- The basis on which the employee’s wages are paid (e.g., $12 per hour or $400 per week),
- Hourly pay rate,
- Total overtime earnings,
- Additions or deductions from the employee’s wages,
- Total wages paid each pay period, and
- Date of payment and the pay period.
The preceding records must be preserved for at least 3 years at the place of employment or in a central records office.
Required workplace posters in Kansas
In the state of Kansas, both federal and state law require employers to exhibit certain posters in the workplace.
Here’s a list of required state posters:
- Unemployment Insurance Poster,
- Attorney General of Kansas Human Trafficking Resources poster,
- Workers Compensation Posting Notice Poster,
- KDOL Human Trafficking Brochure,
- Child Labor Poster (if employing minors under 16),
- Kansas Indoor Clean Air Act – No Smoking Poster, and
- Equal Opportunity in Employment Poster.
Moreover, here’s a list of required federal posters:
- Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO),
- The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA),
- Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA),
- Employee Polygraph Protection Act (EPPA), and
- Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA).
🎓 Required workplace posters in Kansas
Frequently asked questions about labor laws in Kansas
To make this guide as comprehensive as possible, we’ve included an FAQ section where we’ll answer common questions about labor laws in Kansas.
Does Kansas have labor laws?
Yes, Kansas uses both federal and state laws to regulate employment. Some of the most important labor laws in Kansas include:
- Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA),
- Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA),
- Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA),
- Kansas Wage Payment Law, and
- Kansas Child Labor Law.
What is the statute 44-315 in Kansas?
The statute 44-315 regulates employment separation in Kansas. Under this law, employers must pay their employees all due wages by the next scheduled payday.
However, if an employer fails to pay the employee in this time period, they’ll have to pay an additional penalty of 1% of the total unpaid wages for each additional day (except Sunday and holidays).
Is it legal to work 8 hours without a break in Kansas?
Yes, it’s legal. Kansas has no federal or state laws requiring employers to provide breaks to their workers.
Need a simple time clock for employees?
Clockify allows you to track time, attendance, and costs with just a few clicks for FREE.
Your team can track work time personally via the web or mobile app, or you can set up a time clock kiosk from which employees can clock in and out.
In addition, Clockify has a robust time off feature that allows your employees to schedule their time off days.
This gives you insight into who is available and helps you stay compliant with the current labor laws in Kansas.
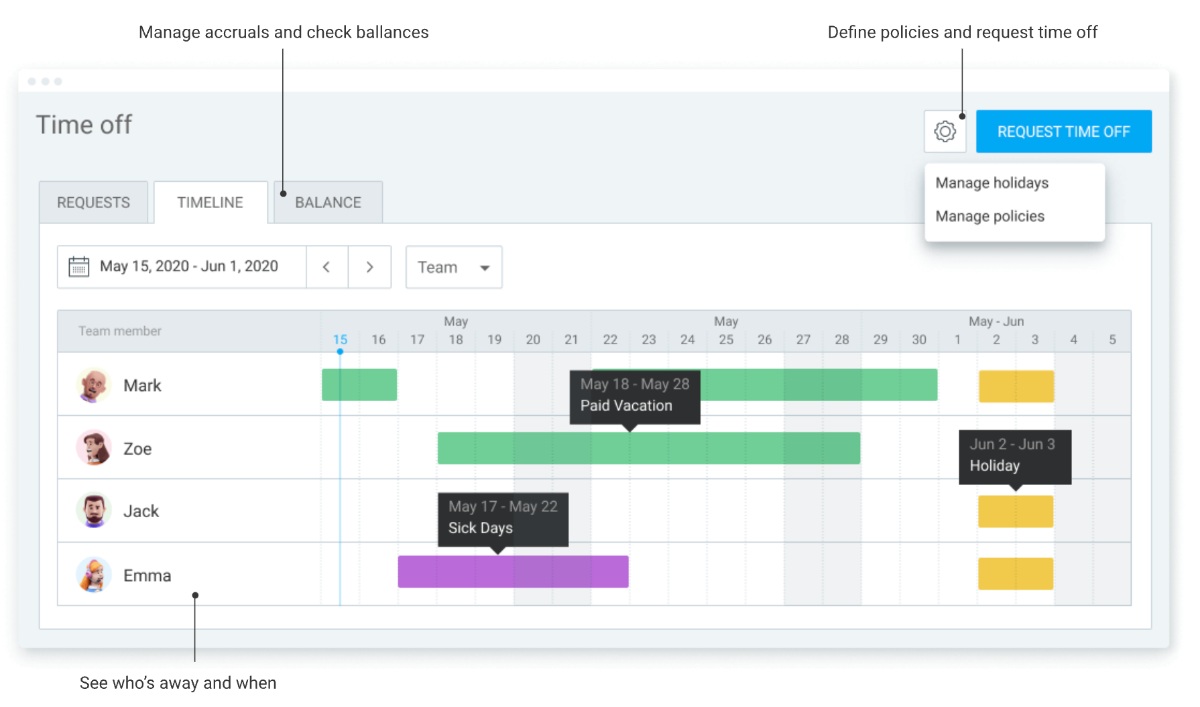
Later, you can approve timesheets and time off, schedule shifts, run time card reports, and export everything for payroll (PDF, Excel, CSV, link, or send to QuickBooks).
Conclusion/Disclaimer
We hope this Kansas labor law guide has been helpful. We advise you to pay attention to the links we’ve provided, as most of them will lead you to the official government websites and other relevant information.
Please note that this guide was written in Q2 2025, so any changes in the labor laws that were included later than that may not be included in this Kansas labor laws guide.
We strongly advise you to consult with the appropriate institutions or certified representatives before acting on any legal matters.
Clockify isn’t responsible for any losses or risks incurred should this guide be used without further guidance from legal or tax advisors.
