Making plans and setting goals is easy with a few full-time employees.
However, everything is harder when you also have various part-time workers and contractors, including:
- Budgeting,
- Project management, and
- Resource allocation.
That’s where the full-time equivalent (FTE) helps. It’s a metric that quantifies an employee’s workload by comparing it to a full-time schedule.
Companies use FTE to assess workforce capacity, plan projects, manage budgets, and comply with legal requirements.
In this article, we’ll discuss FTE basics, show you how to calculate FTEs, and answer frequently asked questions.
Let’s dive in!

What is the full-time equivalent (FTE)?
A full-time equivalent (FTE) — also known as a whole-time equivalent or WTE — represents the sum of all full-time hours employees work in a certain company.
Along with counting the hours worked, FTEs show how many full-time employees a particular company employs within a fiscal year or needs to employ to carry out a project.
Depending on your needs, you can calculate FTE weekly, monthly, or yearly.
How to work out FTE for an individual employee?
The formula for calculating FTE for a single worker is simple:
Employee’s scheduled hours / Company’s official full-time hours = FTE
Let’s say your company defines “full time” as 40 hours per week, and the employee works 40 hours per week. In that case, the calculation is:
40 / 40 = 1.0 FTE
So, 1 standard full-time employee counts as 1.0 FTE.
Track work hours with Clockify
Here are a few examples of FTE calculations with part-time employee hours:
Scenario #1:
1 part-time employee working half of the company’s official full-time schedule:
20 hours worked / 40-hour work week = 0.5 FTE
Scenario #2:
1 part-time employee working a quarter of the company’s official full-time schedule:
10 hours worked / 40-hour work week = 0.25 FTE
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Learn about the difference between full-time and part-time employees here:
How to calculate FTEs for your company?
To calculate FTEs for your entire organization, follow these steps.
Step #1: Define your standard workweek
A typical full-time work week consists of 40 working hours.
If your standard work week consists of 40 hours, your employees probably work 8 hours per day. This can vary depending on your organization. For example, some employees may work 7 hours one day and 9 hours the next day.
So, you need to know the total work hours in a standard week at your company before you can calculate FTEs.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
If you wonder how overtime work is taxed, check out the article below for more info:
Step #2: List your employees
First, list all your staff. Then, perform employment classification based on their weekly work hours.
If your standard workweek is 40 hours, a full-time employee is anyone at your company who works 40 hours or more per week. Anyone who works less than your standard workweek (in this case, 40 hours) is considered a part-time employee.
In most cases, you don’t count independent contractors (1099 workers) since they’re not considered employees.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Learn how to pay independent contractors easily here:
Step #3: Calculate the total annual work hours
Next, calculate how many hours both full-time and part-time employees have worked during the year.
Considering a year has 52 weeks, a full-time employee with a typical 40-hour workweek spends 2,080 hours working a year (40 hours x 52 weeks = 2,080).
On the other hand, a part-time employee working 25 hours per week clocks in a total of 1,300 hours a year (25 hours x 52 weeks = 1,300).
Bear in mind that some years have 53 weeks and adjust your calculation if necessary.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Need to determine how many work hours your employees work during a fiscal year? Head to the following link for more info:
Step #4: Add up the total annual work hours for each employee
Now, you must calculate the sum of annual work hours for all employees.
Let’s assume you have 10 full-time employees working 40 hours per week and 3 part-time employees working 25 hours a week.
Here’s how you would add your full-time employees’ annual work hours:
Full-time employees: 10 x 2,080 = 20,800
Next, for your part-time employees:
Part-time employees: 3 x 1,300 = 3,900
Step #5: Determine the part-time FTE
To calculate the total FTE in your company, first determine the FTE of your part-time workers. To do that, divide the total number of hours worked by your part-time employees by the total number of annual hours worked by 1 full-time employee.
In our example, we have 3 part-time employees working 25 hours per week, which equals 1,300 work hours per year (3,900 hours per year for all 3). On the other hand, 1 standard full-time employee works 2,080 annual work hours.
All things considered, here’s how the calculation would go:
3,900 / 2,080 = 1,875 (1.875 FTE)
Therefore, 1.875 is the FTE of 1 part-time worker.
Step #6: Determine the total FTE
Finally, to calculate the total FTE within your organization, add the number of FTEs worked by your full-time employees to the part-time FTE.
Since 1 full-time employee working 40 hours a week equals 1.0 FTE, in our case of 10 full-time workers, that would be:
10 full-time workers x 1.0 FTE = 10.0 FTE
Since we already have the part-time FTE, here’s the total FTE with 3 part-time employees and 10 full-time employees:
Total FTE = 10.0 FTE (full-time FTE) + 1.875 (part-time FTE)
Total FTE = 11.87
To easily calculate the FTE for all your employees — part-time and full-time — use our free calculators provided below:
⏬ Download the FTE calculator for all employees in Excel
⏬ Download the FTE calculator for all employees in Google Sheets
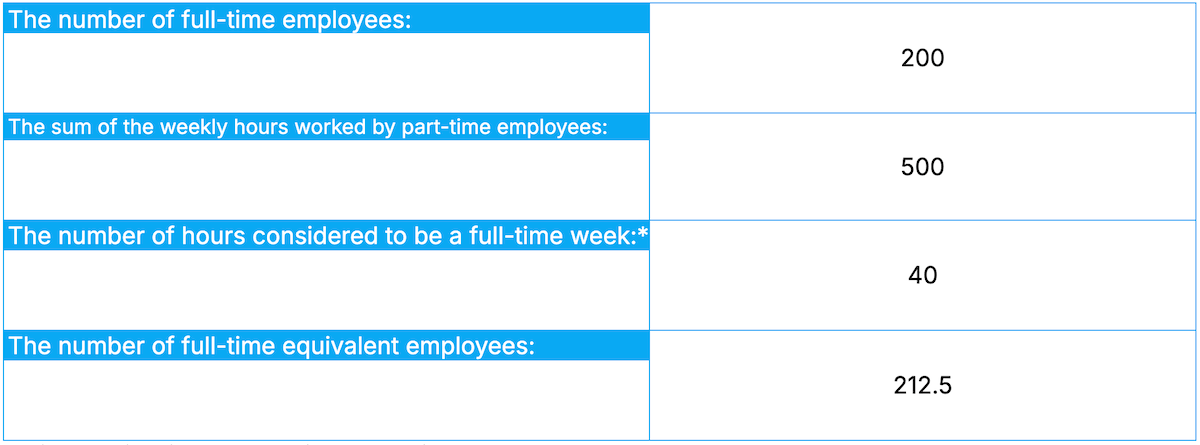
Bear in mind, these are just simple FTE examples. In specific use cases, like project management or federal program eligibility, calculations may be more complex.
Bonus FTE calculators
Since FTE calculations can vary depending on your needs, we’ve also made the following calculators for specific use cases:
- FTE calculator for project managers,
- FTE calculator for salary estimation,
- FTE calculator for Applicable Large Employers (ALE),
- FTE calculator for the small business tax credit program, and
- FTE calculator for Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) loan forgiveness.
FTE calculator for project managers
To easily calculate how many full-time equivalent employees you need for a project, budget analysts and managers can use the following free calculator:
⏬ Download the FTE calculator for project managers in Excel
⏬ Download the FTE calculator for project managers in Google Sheets

All you need is the estimated time to complete the whole project and the number of daily hours your employees will work on that project.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Need help making accurate time estimates for projects? Take a look at the following article:
FTE calculator for salary estimation
To easily convert an employee’s salary into a full-time equivalent salary for a full working year, you can use the following calculator free of charge:
⏬ Download the FTE salary calculator in Excel
⏬ Download the FTE salary calculator in Google Sheets
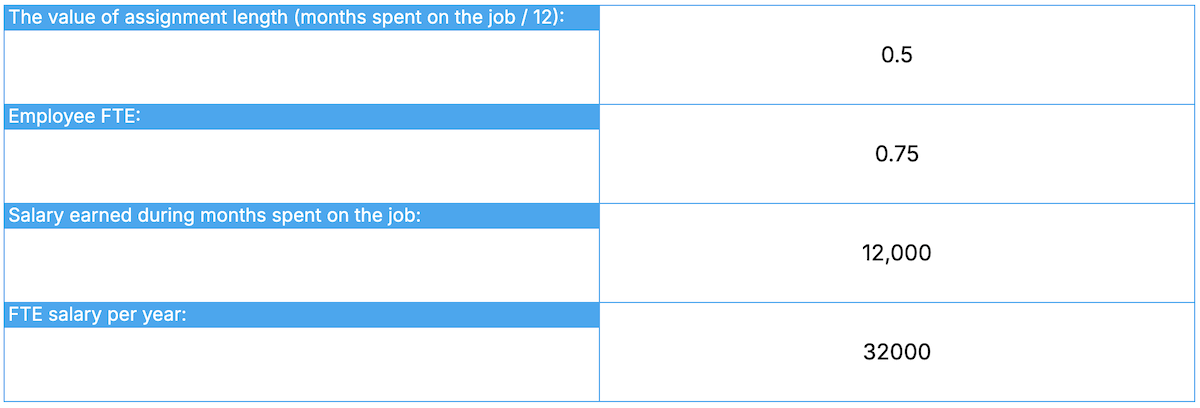
In our example, the FTE salary calculation is: 12,000 / 0.375 = 32,000 as shown above.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Struggling with accurate labor cost estimation? Read the following article that covers all relevant factors you should consider:
Track salary costs with Clockify
FTE calculator for Applicable Large Employers (ALE)
According to the Affordable Care Act, Applicable Large Employers (ALEs) must have at least 50 full-time equivalent employees, including part-time employees.
To quickly determine if you qualify as an Applicable Large Employer, you can use the following calculators:
⏬ Download the FTE calculator for ALE in Excel
⏬ Download the FTE calculator for ALE in Google Sheets

The calculator is straightforward — enter the required data, and it will determine if you’re an Applicable Large Employer.
FTE calculator for the small business tax credit program
To qualify for the small business tax credit program, businesses must have fewer than 25 full-time equivalent (FTE) employees.
You can use the following calculator to see if you qualify for a tax credit, with 3 different methods:
⏬ Download the FTE calculator for the small business tax credit program in Excel
⏬ Download the FTE calculator for the small business tax credit program in Google Sheets
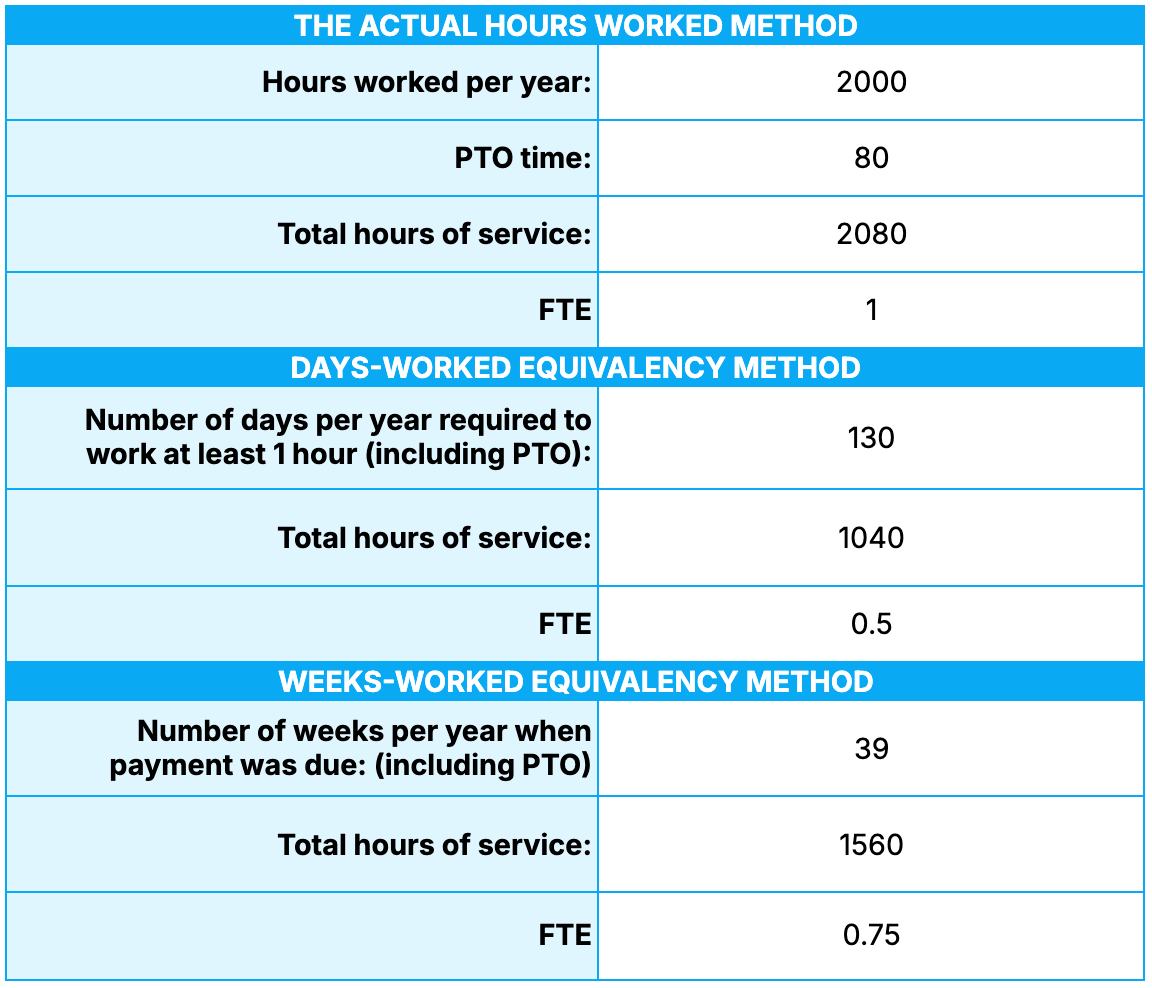
If you, for instance, choose the first method, enter all the actual hours worked (including PTO) and divide that number by 2,080 to get the final FTE.
FTE calculator for the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) loan forgiveness
The Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) provides funds for small business owners to help them cover up to 24 weeks of payroll or other expenses, such as utilities and rent.
Such businesses may have their loans fully forgiven if they maintain the same number of FTEs while receiving financial assistance.
To make payroll calculation for eligibility for full forgiveness easier, you can use the following calculator:
⏬ Download the FTE calculator for PPP loan forgiveness in Excel
⏬ Download the FTE calculator for PPP loan forgiveness in Google Sheets
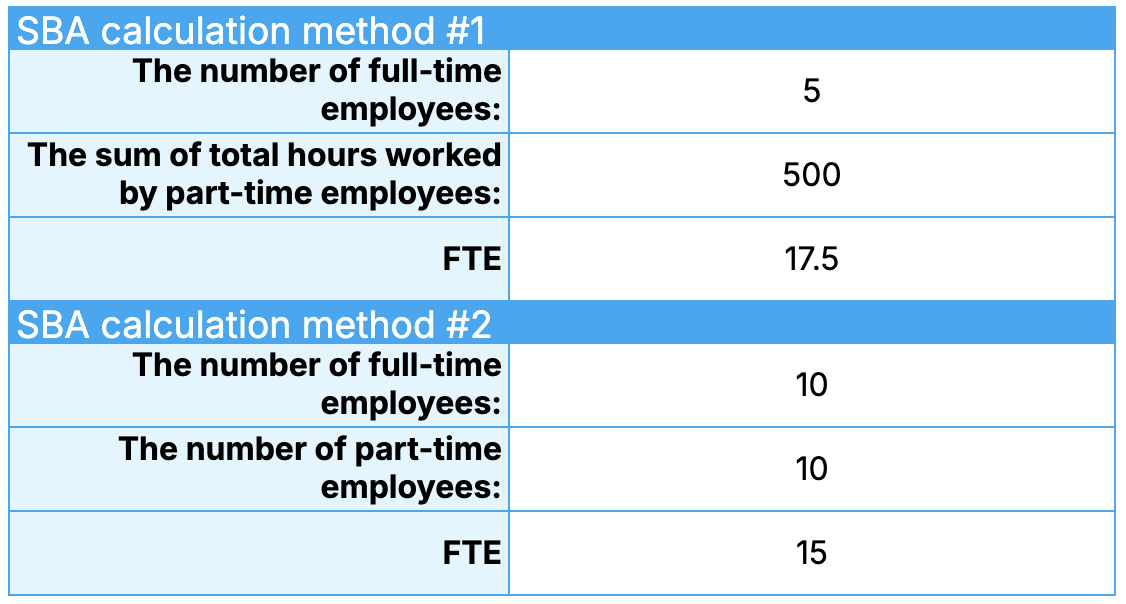
For the SBA calculation method #1, enter the number of full-time employees and the total sum of work hours by part-time employees.
As for the calculation method #2, enter the number of full-time employees again, and just the number of part-time employees to calculate the FTE.
Track work hours with Clockify
FAQ about FTE
Next, we’ll answer some of the most frequently asked questions about FTE.
What is a typical full-time schedule?
According to the IRS, a US employee who works at least 30 hours per week or 130 hours per month is considered a full-time employee.
In practice, these numbers fall somewhere between 30 and 40 hours per week, with 40 hours per week (8 hours per day, 5 days per week) being the most common norm for full-time employee scheduling.
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics’ data from April 2025, private-sector US employees (excluding the farm sector) work 34.3 hours per week on average.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Here are some tips on how to make the most of your 8-hour workday:
What is 100% FTE?
A 100% FTE is the same as a 1.0 FTE — therefore, 100% = 1.0 FTE.
This number may indicate that one person is working a full-time schedule or several people are fulfilling the duties of one full-time position.
In one company, a full-time schedule typically consists of 40 hours per week. In another, it may be 37.5 hours per week. Since both are considered full-time schedules in their respective companies, each schedule counts as 100% or 1.0 FTE.
What is 90% FTE?
A 90% FTE, which you can also express as 0.9 FTE, means an employee works 90% of the hours that the company requires from a full-time employee.
If the company’s full-time standard is 35 hours, this would mean working 31.5 hours per week. The calculation is simple: 35 full-time hours x 0.9 FTE = 31.5 hours.
What is 75% FTE? When is 75% FTE or higher considered full-time?
An employee who works 75% of the hours of a full-time worker has a 0.75 FTE.
This usually amounts to:
- 28 hours per week for non-exempt positions that work 37.5 hours per week under normal conditions, or
- 30 hours for exempt positions that work 40 hours per week under normal conditions.
However, temporary job positions are excluded from this rule.
Whether an FTE of 0.75 is considered full-time depends on the company policy. If 0.75 FTE is considered full-time in a company, employees may be eligible for the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program — eligible employees don’t have to pay out their federal student loans.
However, bear in mind that this only applies to employees who work 30 hours per week in a 0.75 FTE position, i.e., the IRS minimum for a full-time definition.
In contrast, non-exempt positions that typically work only 28 hours per week on a 0.75 FTE schedule do not qualify, even if the employer policy defines them as full-time.
What is 50% FTE?
A 50% FTE, also expressed as 0.5 FTE, means that an employee works half the hours of a full-time employee.
Let’s say a company defines 1.0 FTE as the standard 40 hours per week. In this case, a 50% FTE employee would work 20 hours per week, which is 50% of the hours of a full-time worker.
To understand how different working hours translate to FTE in a standard 40-hour workweek, check out the table below:
| Working Hours Per Week | FTE |
| 40 | 1.000 |
| 35 | 0.875 |
| 30 | 0.750 |
| 25 | 0.625 |
| 20 | 0.500 |
| 15 | 0.375 |
| 10 | 0.250 |
| 5 | 0.125 |
What does FTE mean in salary?
An FTE salary is an employee’s salary converted into a full-time equivalent salary within a full year, regardless of whether the said employee holds a full-time or part-time position. The actual workload is not taken into consideration for this calculation.
Example: Let’s say that an employee has held a job for 6 months (0.5 times of a full year) at an FTE of 70% (0.7) and earned $12,000 during this time.
The FTE salary calculation for this employee goes as follows:
$12,000 / ( 0.5 x 0.7 ) = $34,285 per year
Why is working out FTE important for PTO?
FTEs can also impact the number of hours employees can accrue for PTO.
The actual PTO accrual rate may depend on several factors, including years of employment and employer policies.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Use pre-made PTO templates to implement an effective employee time off request system here:
FTE vs. headcount analysis — What’s the difference?
FTE measures how many hours your employees work against the company’s standard for a full-time position. On the other hand, headcount is a metric that simply shows the total number of employees in an organization.
Make full-time equivalent calculation easy with Clockify
To calculate FTE, you need accurate data on your employees’ work hours.
Clockify is a powerful time tracker that can simplify your FTE calculations and other business processes.
With Clockify, your employees can track work hours in 3 easy ways:
- Simple timer that an employee can start or stop when working on different tasks. It automatically logs the time spent on each task into the worker’s timesheets.
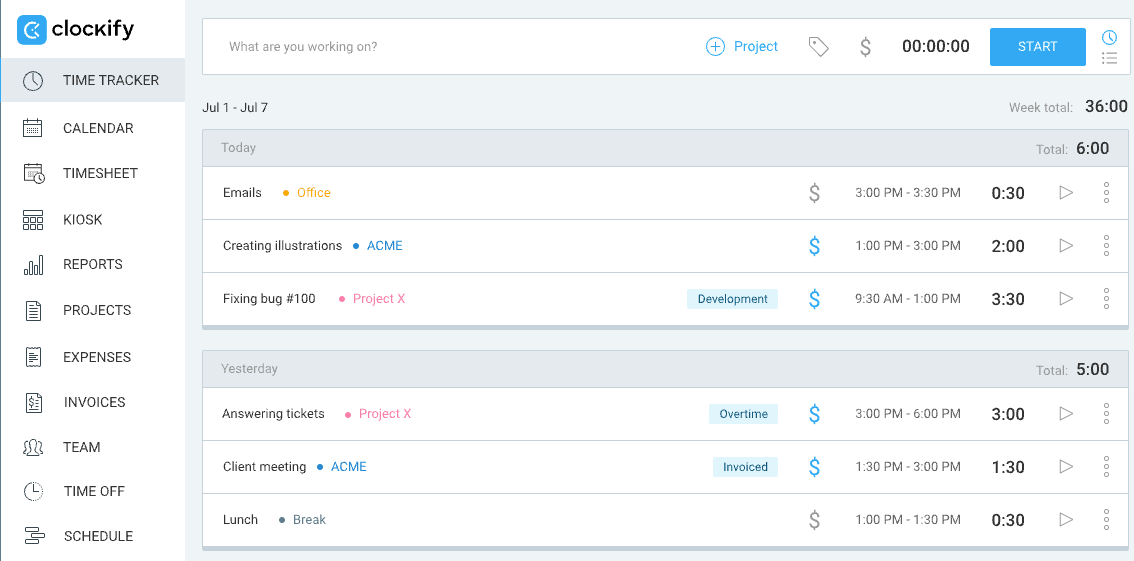
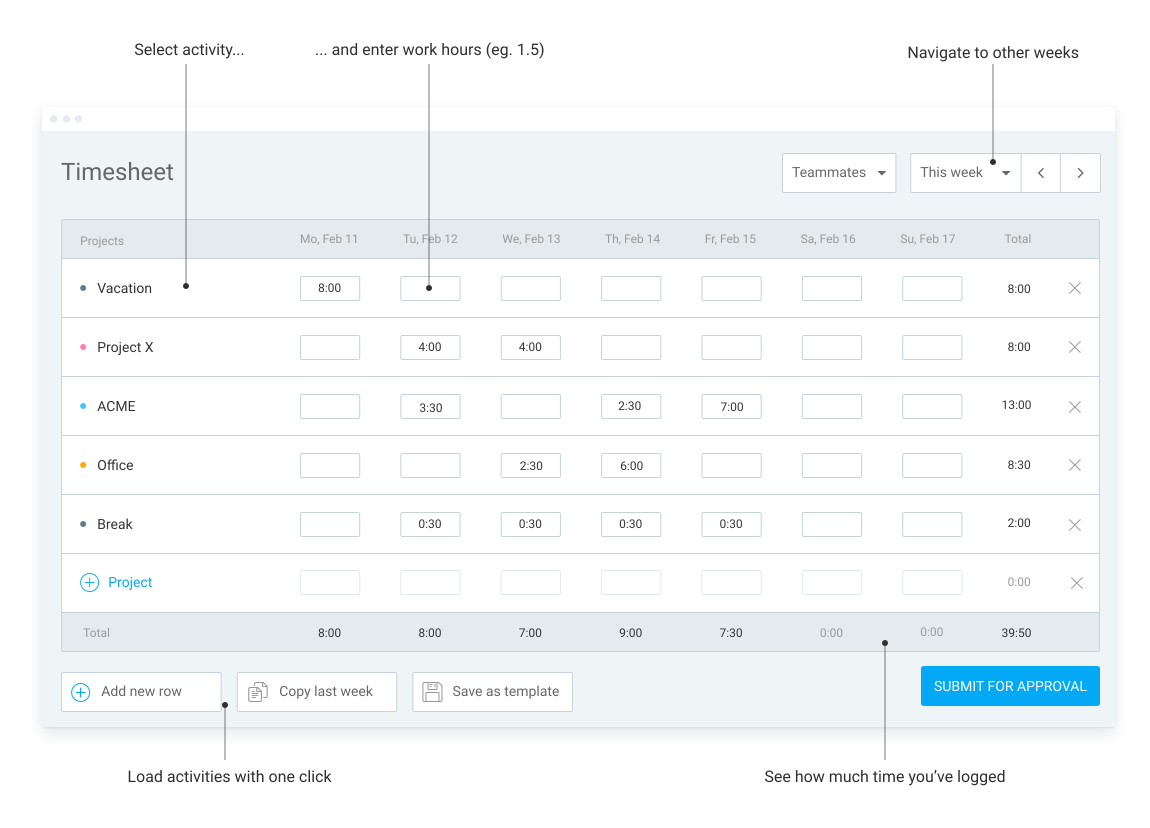
- Digital timesheets that let employees manually log the hours they spent on various projects and tasks.
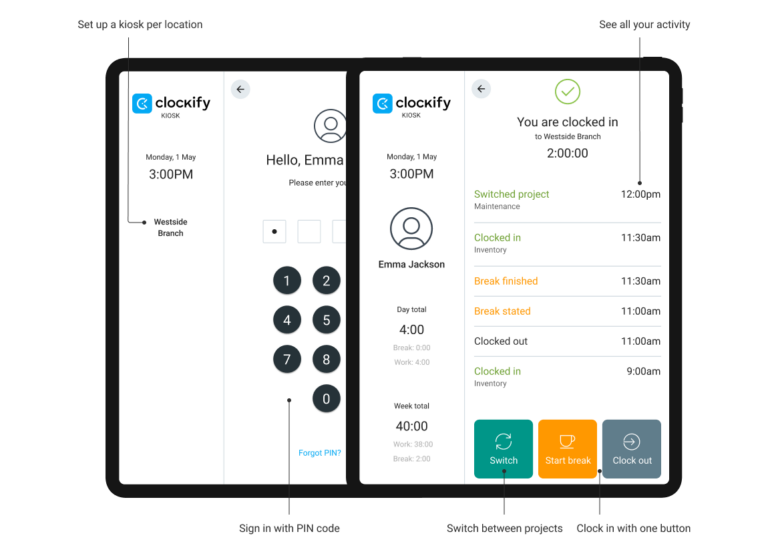
- Clock-in kiosk where employees can clock in at the press of a button, and their timesheets will be updated automatically.
Based on data from employee timesheets, Clockify creates and updates visual reports in real-time.
For example, the summary report can display the total number of hours worked by any user for any week, month, or year.
Based on this information, you can quickly calculate the FTE for that employee, their team, or the whole company.
With Clockify’s intuitive interface, useful insights into your employees’ time are only a few clicks away. Plus, the team behind Clockify offers 24/7 support via phone, email, or chat if you have any questions or need any help.



