Ideas are the foundation of human progress, innovation, and creativity, alongside being one of the most important elements of business success.
As a businessman and one of the first global makers of automobile tires, Harvey S. Firestone, once said:
”If you have ideas, you have the main asset you need, and there isn’t any limit to what you can do with your business and your life. Ideas are any man’s greatest asset.”
So, how do you come up with new ideas?
Brainstorming is a powerful tool for generating ideas and sparking innovations, which are the main force of creation and success.
In a world where creativity and collaboration are becoming increasingly important, the ability to effectively brainstorm and create new ideas is more valuable than ever.
So, understanding the basics of brainstorming, what brainstorming techniques are best for your team, and how to make it work for you can be a game-changer.
In this blog post, we’ll explore:
- The 6 rules of holding a brainstorming session,
- 17 best brainstorming techniques,
- Brainstorming tips by experts, and
- The benefits of brainstorming.
Let’s dive in and discover the power of brainstorming!
Table of Contents
6 Rules for holding high-quality brainstorming sessions
A brainstorming session is usually a group activity with a purpose of creating a solution to a problem or generating innovative ideas. It is a structured approach, and brainstorming sessions are usually led by a leader or facilitator who encourages free thinking, creativity, and open communication.
If you want to achieve peak office productivity and a constructive exchange of ideas, you’ll need some rules for leading brainstorming sessions. According to the New “Brainstorming” Principles paper, here are six brainstorming rules.
Rule #1: Give clear instructions about the brainstorming process
A team leader is responsible for giving clear instructions about the aim of a particular brainstorming session.
One rule should be focusing on quantity over quality. Participants should be encouraged to think of as many ideas as they can without worrying about the quality of those ideas. This will ensure plenty of ideas that can be refined and expanded later on.
During the ideation phase, you as a team lead should refrain from feedback and criticism. All ideas should be accepted without judgment, as out-of-the-box thinking is encouraged.
Schedule a brainstorming session now
Rule #2: Determine the specific goals of a brainstorming session
We usually think that brainstorming is a natural and effortless process that doesn’t need any clear directions — that ideas just pop into our minds. But, brainstorming sessions are more productive when they are structured and have a clear and specific goal.
This process of determining the aim of a task, plan or brainstorming, known as the “goal setting”, is one of the most effective principles discovered by organizational and industrial psychologists Latham and Locke. This theory can also be used in team brainstorming sessions.
According to the theory, setting specific goals is far more effective than setting vague and ambiguous goals. For example, team leaders should decide how many ideas should be generated during a session.
Furthermore, we get motivation when we know exactly what we need to do and what kind of results we want to achieve, which later leads to improved performance. That is why setting a clear goal for a brainstorming session is critical for getting the most out of it.
💡Clockify Pro Tip
There’s much more to setting goals than it meets the eye. In case you wondered how to set smart goals (and by ‘smart’ we mean: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound) head to the following blog post for more info:
Rule #3: Team members should generate initial ideas alone
During the ’80s and ’90s, people thought group brainstorming was inefficient compared to brainstorming alone. One of the possible explanations is that some participants might feel shy to express their ideas or just lack accountability, so they would let others take over. Another reason why group brainstorming was considered inefficient was that while participants were waiting for their turn to speak and present their ideas, they would forget them.
But an experimental research Brainstorming Groups in Context: Effectiveness in a Product Design Firm shows that brainstorming in groups can be more effective if team members do the initial ideation alone than in groups. Individuals are more productive when working solo, so the brainstorming facilitator should allow team members to do the initial brainstorming alone and give them enough time to write down and prepare their ideas.
They can then present their ideas one at a time before engaging in a group discussion. When they share and build on each other’s ideas, true creativity emerges. As a result, everyone contributes equally to the brainstorming session, and your team can achieve maximum innovation and creativity.
Rule #4: Build on the ideas of others
As mentioned in the previous rule, team leaders should encourage participants to discuss their ideas, refine them and build on each other’s ideas.
A brainstorming group should also include a diverse group of people from different teams or with different experience and educational backgrounds to ensure maximum creativity and innovation in a brainstorming session.
People with different experiences, educational backgrounds, and teams will have different perspectives and will approach the problem or idea from various angles. According to the article, simply being exposed to diversity can alter your thinking and improve your creativity and problem-solving abilities.
Rule #5: Participants should vote on the best idea
After they have presented and discussed their ideas together as a group, participants should individually vote for the best idea. This ensures commitment from each participant.
Rule #6: Keep brainstorming sessions short
According to the previously mentioned study on brainstorming principles, brainstorming sessions should be brief, lasting no more than fifteen minutes for initial idea generation and no more than two hours for the entire brainstorming session. You can use a time tracker like Clockify to track your time during brainstorming sessions.
With Clockify, you simply start the timer when you begin brainstorming and stop it when you’re done. This will allow you to keep track of how much time participants spend presenting their ideas to the group.
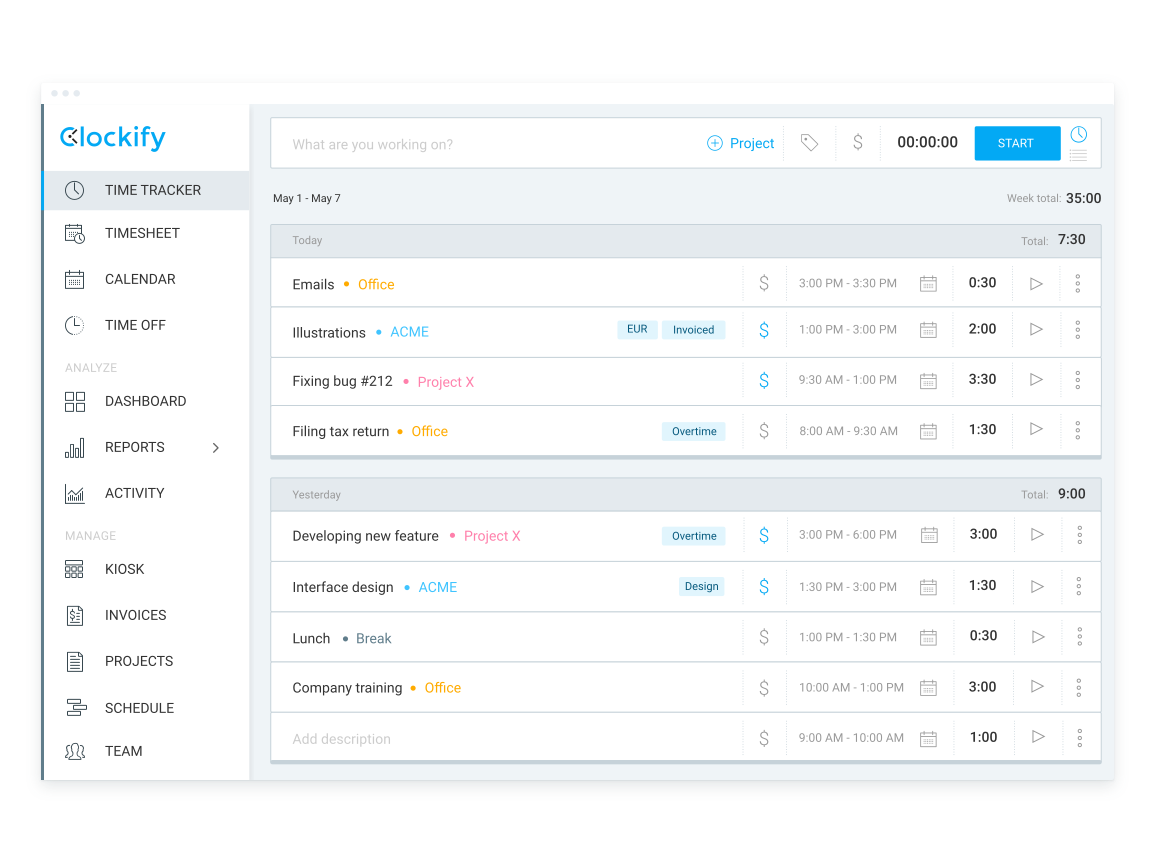
With Clockify, you can ensure that your brainstorming sessions are adequate in length, and that each participant has an equal amount of time to present their ideas.
Best brainstorming techniques for teams
Whether you brainstorm to solve a problem, get new ideas, or expand on an existing one — it’s good to know which technique works best for each situation and team. So, we’ve listed some of the best brainstorming techniques which you and your team can make use of.
Technique #1: Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a brainstorming technique that employs visual tools, such as diagrams, which are used for generating and organizing information, ideas, and concepts.
Although similar techniques were used by Leonardo da Vinci and Pablo Picasso, Tony Buzan, a British author and educational consultant, introduced the term “mind mapping” in the 1960s as a way to improve memory and learning. Also, Buzan wrote The ultimate book of mind maps.
The 3 most important elements for creating a successful mind map are:
- Central idea/theme/problem,
- Associations (presented as branches and sub-branches), and
- Colors.
Thus, a mind map typically starts with a central idea or concept, which you can place at the center of the page. From there, you can think of subtopics, associations, related concepts, or details about the central idea — and present them in “branches”. Next, each branch may have sub-branches, which can contain additional details or related ideas, usually keywords.
The more colorful the nodes and connections are, the easier it will be for your brain to absorb information.
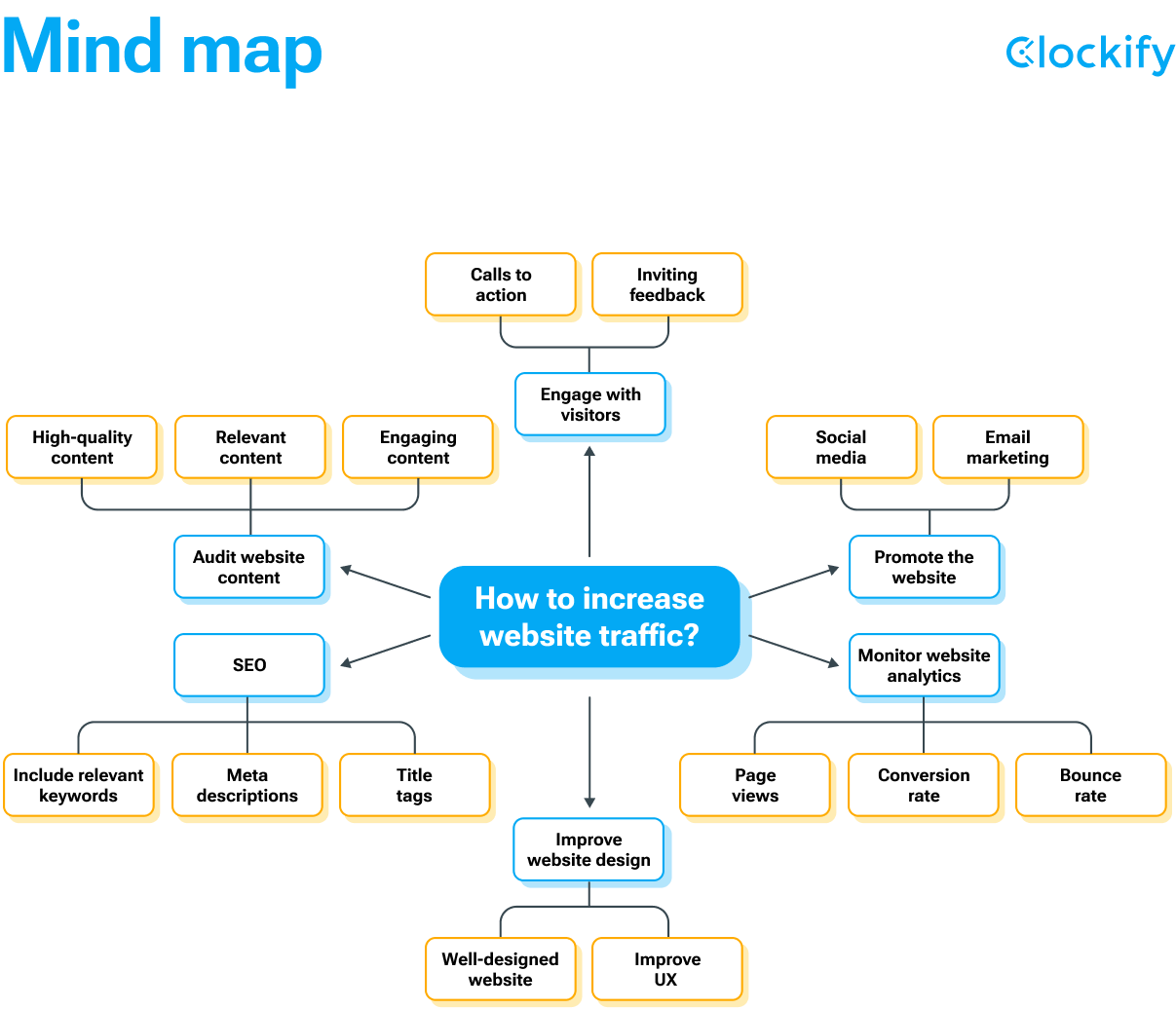
In the screenshot above, you can see a simple mind map which can help you brainstorm a business idea. Simply center the main topic or problem on a piece of paper, and then branch out the ideas or solutions that come up during the brainstorming session.
For example, you have a central idea in the form of a question: How to increase low website traffic? You can branch out from this central concept with ideas (subtopics) like:
- Audit website content,
- Improve website design,
- SEO,
- Promote the website,
- Monitor website analytics, and
- Engage with visitors.
In the same way, you can take any central idea, issue, or a question, and break it down into smaller nodes, to help you see the connections between the smaller parts that make the whole.
Why should you use the mind mapping technique?
This technique is best suited for teams with “visual persons”, as it provides a visual representation — a diagram — of an idea or a problem. Mind mapping also provides a clear and detailed breakdown of information about an idea you’re exploring.
Technique #2: The SWOT analysis
The SWOT analysis is not exactly a brainstorming technique but rather a strategic planning tool.
SWOT is an acronym that stands for:
- Strengths — how does your idea, product, project, or company stand out from your competitors?
- Weaknesses — what are the weak points of your idea, product, project, or company which can put you at a disadvantage or risk?
- Opportunities — what external opportunities do you have that can improve your idea, product, project or company?
- Threats — what external factors might threaten your idea, product, project, or company?
It is commonly used in business, marketing, and organizational development to assess the current situation of a product, idea, project or business, and determine a course of action. However, it can serve as a useful brainstorming exercise for analyzing ideas, projects, products, or businesses.
Furthermore, the SWOT analysis focuses on the internal and external factors that can affect your idea. For example, a team of developers in a software company wants to implement a new feature, and wants to see all the possible benefits it could bring, but also the ways in which the feature could harm their current product. In that case, SWOT analysis can help them analyze the feature — how this feature can improve their product and whether there are any disadvantages of adding this feature.
SWOT brainstorms give the best results when they’re done in a matrix, like the one below.
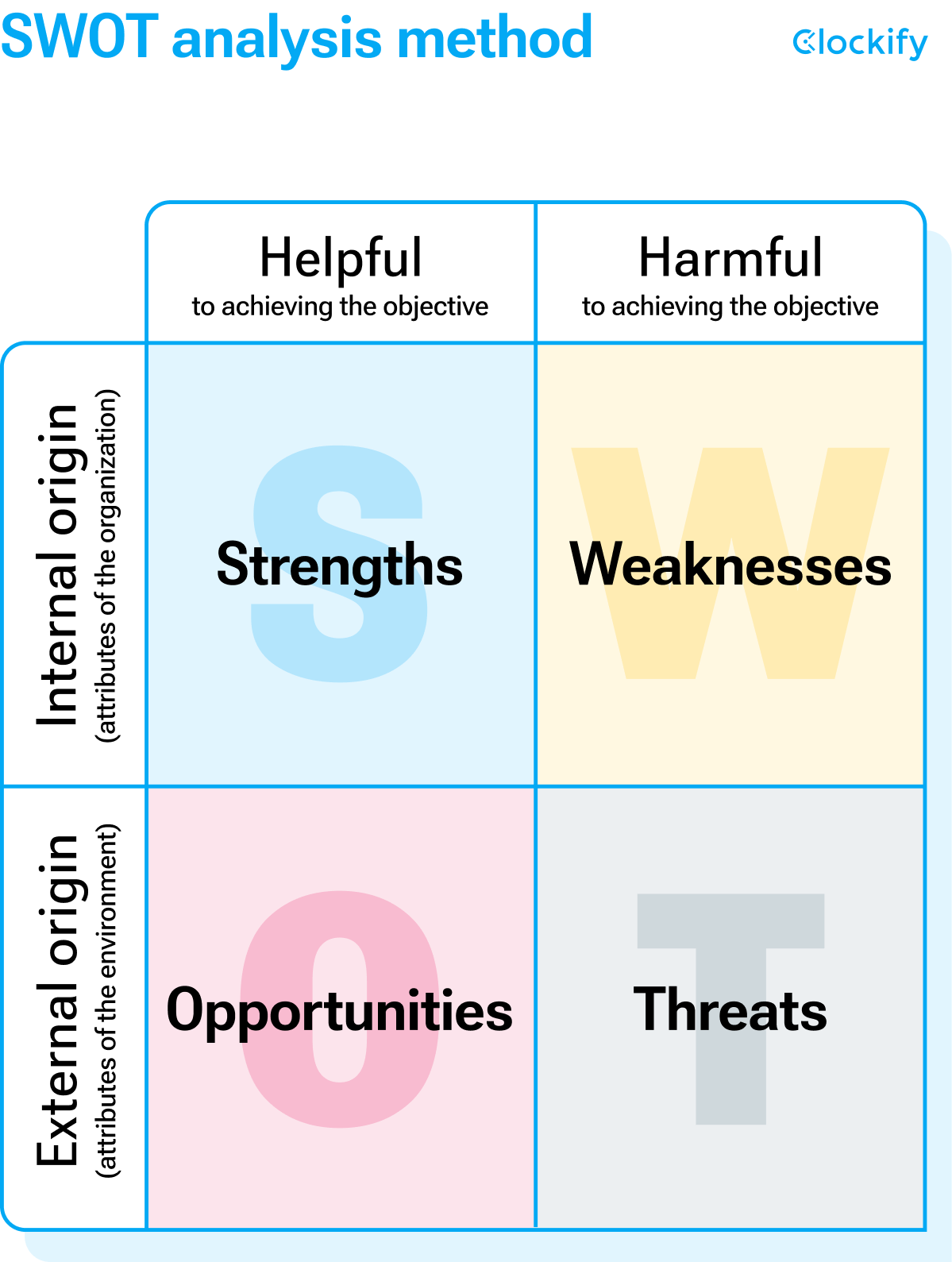
Presented like this, SWOT has a great visual backup that makes all the information clearly visible, and “within reach”.
Why should you use the SWOT technique?
Overall, a SWOT analysis can give you a thorough understanding of the internal and external environments that your company is operating in, assisting you in making choices and creating winning business strategies.
But, it can also be an effective team brainstorming technique which focuses on both positive and negative aspects of an idea, project or product.
As a result, you have a complete picture of your project or idea, including all of its advantages and disadvantages.
Technique #3: The brainwriting
Brainwriting aims to eliminate situations where the same people always talk, while the others stay quiet or tune out, with one simple change — all initial communication is nonverbal.
Usually, when there is a brainstorming session, most of us will know right away how the session will go. We know who will be active and talk the most, who will interject, and whether or not our input is even needed. But, brainwriting changes this.
As a meeting facilitator, you give everyone a piece of paper, and have them write three ideas or strategies (depending on what you’re doing) related to the theme of the brainstorm. After five or six minutes, everyone passes their paper to the person next to them, and then that person expands on their neighbor’s ideas. This is done until the papers return to their owners. The second part of the session includes analyzing the findings each paper brings.
For example, team members can discuss common themes, issues, similarities, and differences between ideas. This way, everyone gets to contribute to the brainstorming session.
Why should you use the brainwriting technique?
The brainwriting technique is best for newly formed teams, teams with a lot of introverts, or different personality types. Through brainwriting, everyone is involved, and there is no risk of having certain people be unable to voice their opinions. Everyone contributes equally, which ensures transparency and equality.
💡Clockify Pro Tip
If you want to know what makes each of the 16 personality types productive, read our blog post:
Technique #4: The eidetic image
The biggest proponent of using the eidetic image method was psychologist Jacqueline Sussman, who worked with — among others — Mattel and Google. She notes that eidetic images are vivid images stored in our brain, based on previous experiences, and gives the example of wanting to make a salad. The moment you read the ingredients list, you’ll imagine each one, and assemble them in your head.
In the same way, you can use a brainstorming session with eidetic imagery when you want to build on or improve an existing feature.
One example often used with this method is a smartphone. People are asked to imagine a generic smartphone, and then to start building better features into it — a different color, size, more space, etc.
Then, when the session is over, one member is singled out to present their improved design and discuss it with others.
To facilitate this kind of creative problem solving, try the following order:
- Have everyone present imagine the company’s current product,
- Have them visualize specific improvements to it (size, feature, logo, etc.),
- Guide them through each possible improvement, and see which ones they picked in the end, and
- Have everyone open their eyes and discuss their results.
In this way, each person is given an opportunity to do their own brainstorming, collect their thoughts, and think through each feature. When the presentation time comes, they will have an easier time elaborating. Less time is spent finding the right words or brainstorming on the spot.
Why should you use the eidetic image technique?
The eidetic image technique is best suited for participants who are visual thinkers. It is useful for expanding on existing ideas rather than coming up with new ones or solving problems.
For example, you can use it when deciding on and developing new features for a product.
Technique #5: The rapid ideation
Rapid ideation is a brainstorming method designed to help participants come up with multiple ideas in a short amount of time.
The gist is to set a time limit (usually between 5 and 10 minutes), so the participants can write down as many ideas as possible during that time frame.
After the 10 minutes are up, you can start filtering through the ideas together, singling out the best ones.
Why should you use the rapid ideation technique?
The rapid ideation technique is ideal for participants who are quick thinkers. It is useful especially if you have tight deadlines.
Technique #6: The gap analysis
The core of the gap filling or gap analysis method is:
“How do we get from here to there?”
The facilitator of the session needs to lay out where the team is now and where they need to be. Think of it as a roadmap — you want to get from point A to point B, so you need to know where you can make pit stops for food and rest, where to refuel, and how to divide your driving hours.
In much the same way, you show the team where you would like to be with the project or a product, and then fill in that large gap with small steps that will take you there.
Why should you use the gap analysis?
Gap analysis is a powerful technique that helps organizations identify the gap between their current state of business (possible problems or ongoing projects) and their desired future goals. This technique is great for problem solving, as it is a step-by-step process.
Gap analysis can help organizations:
- Allocate resources effectively — by identifying the areas where the gap is the largest, organizations can prioritize their efforts and allocate resources to the areas where they are most needed.
- Set goals — companies can determine the steps they must take to reach their goals by assessing the disparity between their current state and their desired future state.
- Manage risk — companies can anticipate potential challenges and take steps to mitigate them before they become serious problems by identifying the areas with the greatest gaps.
Technique #7: The 5 Whys
The 5 Whys method relies on the childlike incessant “why why why” to anyone older than them.
“Why is the sky blue?”
“Why can’t animals eat human food?”
“Why do we do X or Y?”
Its aim is to delve deep into the reasoning behind specific decisions, to ensure they’re there for solid reasons, and to prevent potential problems. The “5” in the name is given as a simple limit on how deep you should take the analysis.
Here’s a simple example — creating a feature that lets you close a DM in our chat app:
- Why? So it doesn’t clutter the side of the user’s chat window.
- Why (is that a problem)? It gets crowded and more difficult to find people.
- Why (is it difficult)? Because the user needs to scroll down a list of people, and it takes away time from work.
- Why (does it take away time)? A lot of people rely on fast and easy communication, and this is a proven issue.
- Why? Bumps in communication, even this small, add up to wasted time, and just frustrate the user.
Five isn’t the only limit, though. You can go even deeper. The best visual aid for this kind of brainstorm is the Ishikawa (or fishbone) diagram, made by the Japanese organizational theorist Kaoru Ishikawa.
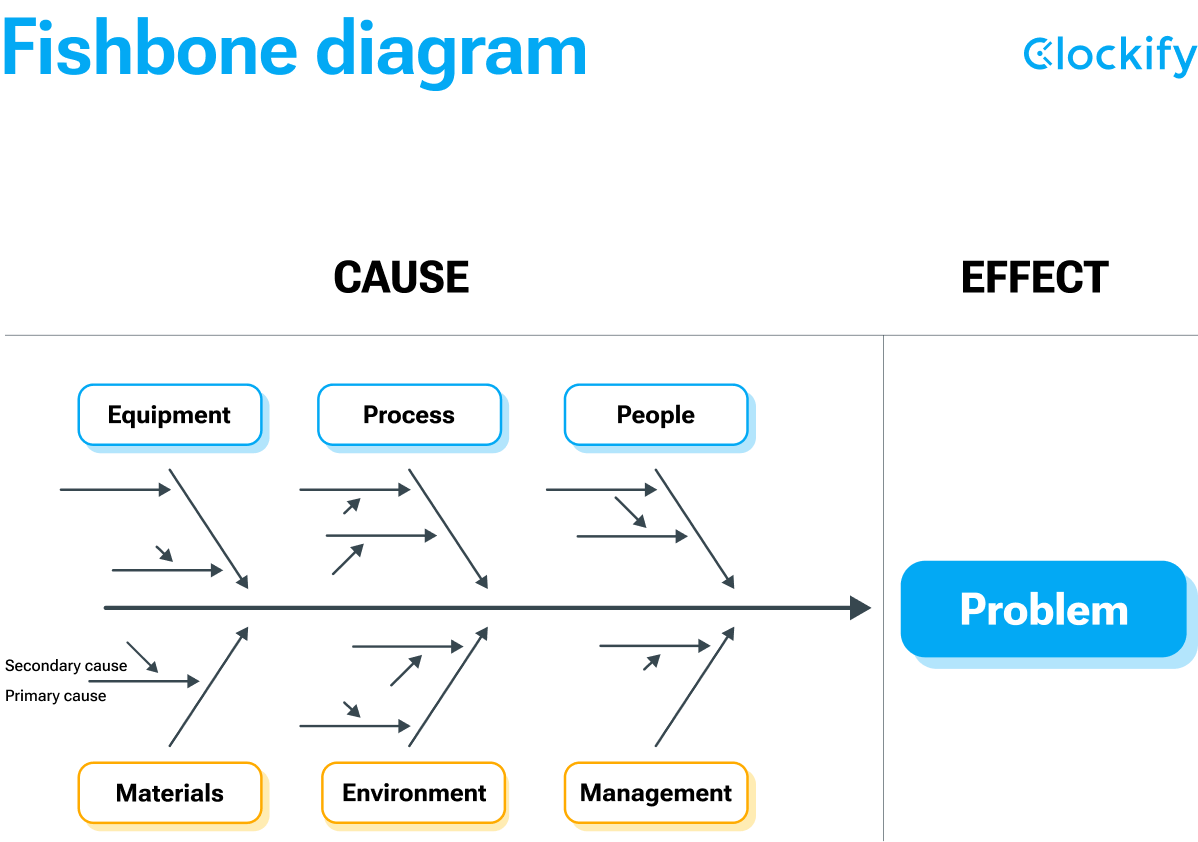
On the far right, where the “fish head” should be, you write down the problem, product, or feature, and to the left, you branch out into the potential causes of the issue — “the fish bones.”
Why should you use the 5 Whys technique?
The 5 Whys technique is a simple yet powerful problem-solving tool that helps to identify the root cause of a problem by asking a series of “why” questions. By identifying the root cause of a problem, you can take steps to prevent it from happening again in the future.
For example, it is great for future feature/product analysis. So, when you use it in your teams, remember to do so in order to understand why you should implement a new feature, or come up with a product, etc.
Technique #8: The stepladder
The stepladder technique is a brainstorming and decision-making technique that allows everyone in a group to contribute their ideas and opinions without being influenced by the group’s initial ideas.
Stepladder brainstorming has an interesting execution:
- The group is introduced to the brainstorm session topic, and asked to spend a few minutes working alone on ideas and suggestions.
- Two participants are left alone in the room and asked to discuss their ideas. Everyone else waits outside of the room (they can even go back briefly to their workstations to avoid awkward standing around).
- After a few minutes, a third person is introduced, and they contribute their own ideas and opinions.
- Another few minutes later, you add a fourth person, and so on.
- When all the members have been gradually introduced, there is a collective discussion of conclusions. See how far you’ve reached as the group gradually grew in number.
Why should you use the stepladder technique?
The stepladder technique can help less extroverted team members express themselves more freely and avoid people conforming to each other’s opinions. It ensures everyone is heard and gets a chance to speak their mind.
What’s more, this technique can help participants who have difficulty speaking in front of large groups adapt and communicate more openly.
Technique #9: The figure storming
The figure storming or alter-ego is a fun technique that serves to put you in someone else’s shoes and see the situation from their point of view.
This technique requires a team to imagine a well-known person, a historical figure, or someone they admire to lead a brainstorming session.
Ask questions like:
“How would Steve Jobs solve this problem?” or “What would Elon Musk do in this situation?”
If you are developing a product, you can put yourself in your customers’ shoes and ask:
“What would our customers want to achieve with this product?” or “How could that product help our customers?”
Why should you use the figure storming technique?
The figure storming technique is a fun and creative way to generate new ideas and solutions by encouraging teams to think from different perspectives. By taking on different roles, participants can see the problem from a new angle and generate ideas they wouldn’t otherwise have.
Technique #10: The online brainstorming or netting
Online brainstorming (also known as netting) is a brainstorming technique mainly used for developing new ideas, but with a plot twist — the brainstorming session is conducted using collaboration tools.
This technique allows you to give all of your team members equal opportunities to offer input and contribute to a session — regardless of their work setting.
By using an online collaboration tool, you and your team can share thoughts in a video call or exchange opinions in a group chat.
The team leader can also use whiteboards, PowerPoint presentations, graphs, and other elements to make the session more efficient.
In case group chat is a more convenient option for your team, a simple question such as “How can we attract more customers?” could generate a large number of ideas within a short time frame.
Why should you use the online brainstorming or netting technique?
Online brainstorming is ideal for remote teams that want to collaborate in real-time. It encourages all team members to participate, as some more introverted team members may feel more comfortable expressing their opinions by writing them down in the chat.
Technique #11: The round-robin
The round-robin technique requires team members to form a circle. The leader then explains the purpose and topic of discussion. People go around the circle, one by one, sharing their thoughts or ideas until everyone has had their turn.
The most important rule in this technique is to give the same amount of time and attention to each person, and restrain from giving feedback until everyone gets a chance to contribute. When everyone has given their idea, you can discuss them and give feedback.
Why should you use the round-robin technique?
This technique is a great option if you have a mid-sized to large-sized group.
Furthermore, it is useful if you have introverted team members who tend to stay quiet, as opposed to more extroverted team members who prefer to express themselves more. This technique is excellent because it requires equal input from all team members.
Technique #12: The starbursting
Just as reporters investigate a story, you can analyze and learn as much as you can about a product, idea, or a project by asking:
- Who,
- When,
- Why,
- What,
- How, and
- Where.
When contemplating an idea, project, or product, consider as many questions as possible. You place the main idea in the center, and the questions burst around it, forming a star diagram.
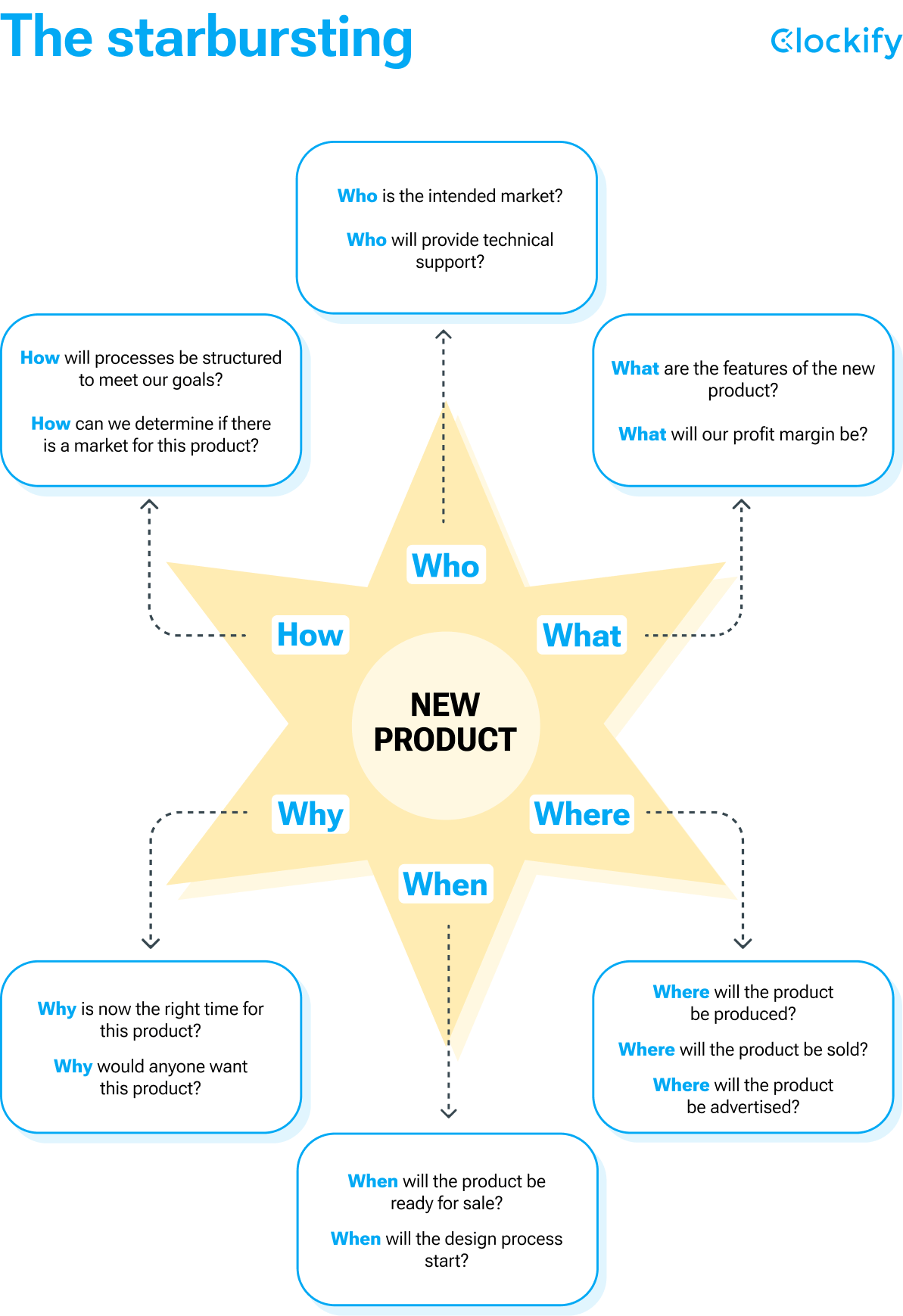
The graph above shows how we formed a star, with the main topic in the center “New product” and questions, such as “What are the features of the new product,” forming each point of the star.
Why should you use the starbursting technique?
The starbursting technique is excellent for product development teams because one question leads to another, and answering those questions results in a solid product development strategy. Consequently, it is a good technique if you tend to overlook details when strategizing.
It is also a good way to create a FAQ page, as you will have prepared questions and answers in advance.
Technique #13: The six thinking hats
The six thinking hats brainstorming technique was invented by Edward de Bono, a Maltese writer, psychologist, and philosopher. He presented this method in the book that carried the same name Six Thinking Hats, in 1985.
As a consultant, he used this approach to advise government agencies. But, he also wanted the six thinking hats to be a useful technique for problem solving in everyday life.
The six thinking hats method is a type of a roleplay technique. We approach an idea, problem, product, project, or business from six different angles.
As for brainstorming sessions, participants are divided into 6 groups — six thinking hats:
- White hat — represents neutral and objective thinking. When wearing this hat, individuals focus on gathering and analyzing data and information.
- Red Hat — represents emotional thinking. When wearing this hat, individuals focus on their instincts, intuitions, and feelings.
- Black Hat — represents critical thinking. When wearing this hat, individuals look for potential problems, risks, and obstacles.
- Yellow Hat — represents optimistic thinking. When wearing this hat, individuals focus on identifying the benefits, opportunities, and positive aspects of a situation.
- Green Hat — represents creative thinking. When wearing this hat, individuals generate new ideas, possibilities, and alternatives.
- Blue Hat — represents strategic thinking. When wearing this hat, individuals manage the thinking process, set goals, and ensure that all the hats are used effectively.
Each group has to think about the same idea from a different perspective.
💡 Clockify Pro Tip
To learn more about emotions and how to manage them at work, read our blog post:
Why should you use the six thinking hats technique?
According to De Bono: “The main difficulty of thinking is confusion.”
When people try to think about a problem or an idea, they often think about everything at the same time. Information, logic, hope, creativity, and emotions all at once can create brain fog.
So, what is the answer? Bono taught us a technique which improves clarity of thought, communication, and creativity. Using the six thinking hats technique, you can lead a more organized and structured brainstorming session that yields better results.
💡 Clockify Pro Tip
When we are overwhelmed by a problem or an idea, we often experience mental fatigue and brain fog. To learn how to overcome these read our blog post:
Technique #14: The reverse brainstorming
The reverse brainstorming technique is another method which requires you to look at the idea from a different viewpoint. Instead of focusing on how to solve a problem, you try to come up with ways to create new problems or amplify an issue. This allows you to identify the underlying causes of the problem and find new ways to solve it.
Here are a few steps on how to hold a reverse brainstorming session:
- Define the problem — begin by defining the issue you want to solve. Make a clear and concise note of it.
- Reverse the problem — instead of asking how to solve the problem, consider how to cause or exacerbate it. For example, if the issue is cyber security and how to protect your website from hackers, the inverse problem could be “How can we hack our website?”
- Generate ideas — brainstorm as many ideas as possible on how to create or worsen the reverse problem. Encourage everyone to contribute ideas, even if they seem silly or unrealistic.
- Analyze the ideas — once you have a list of ideas, analyze them to identify the underlying causes of the problem. This will help you come up with new solutions to the original problem. In the case of cyber security and web hacking, for example, you analyze what weak points your website has that allow hackers to hack into your system.
- Develop solutions — use the insights gained from the reverse brainstorming to develop new solutions to the original problem.
Why should you use the reverse brainstorming technique?
Reverse brainstorming can be a useful technique for overcoming creative blocks and finding innovative solutions to complex problems. It can also assist teams in coming up with new ideas and perspectives that they might not have considered otherwise.
Technique #15: The storyboarding
Storyboarding is a visual storytelling technique that lets you use a series of drawings, images, or other visuals to tell a story or communicate a message.You can use it in a variety of fields, including:
- Film,
- Animation,
- Advertising, and
- Video game development.
Storyboarding is used to visualize and plan out a narrative, scene, or project allowing for more efficient and effective development. This technique is an excellent brainstorming method because it incorporates visual representations of your ideas, which provides more clarity and understanding to your team members.
The process of storyboarding typically starts with a script or a plot summary of the story. The storyboard artist then draws a series of panels, each representing a key moment in the story, and adds a brief description of the action or dialogue that takes place in that panel.
Storyboarding can also be used in product design and marketing. For example, a marketer can use storyboarding to plan and visualize a promotional video or advertisement for a product or service. They can also outline and visualize the whole process of a marketing campaign from start to finish.
Why should you use the storyboarding technique?
The storyboarding technique is excellent for participants who are visual thinkers.
You can use the storyboarding technique to visually plan out your projects and get a sense of how the story will look and feel.
This brainstorming technique provides you with a visual representation of your idea, project, or product, allowing you to better understand it. Storyboarding can also help identify potential issues with your idea or a project early in the process, allowing for adjustments.
Technique #16: The S.C.A.M.P.E.R.
The S.C.A.M.P.E.R. technique is a method for testing and questioning ideas from various perspectives in order to expand and improve them. It is an acronym that stands for:
- Substitute — involves replacing a part or aspect of the problem or solution with something else. For example, what if we substituted paper with a digital solution?
- Combine — involves bringing together two or more elements or ideas to create something new. What if, for example, we combined the features of two distinct products to create a new, multi-functional product?
- Adapt — involves adapting an existing idea or solution to meet the needs of the current problem or challenge. What if, for example, we adapted an existing product for use in a new market?
- Modify — involves altering an element or aspect of an idea in order to improve or increase its effectiveness. What if, for example, we changed the design of a product to make it more user-friendly?
- Put to another use — involves applying an existing solution or product in a new or different way. For example, what other uses can this product have?
- Eliminate — involves removing a component of a solution in order to simplify or improve it. For example, what could we remove from our application to simplify it?
- Reverse — involves flipping or reversing an element or aspect of the problem or solution to generate a new viewpoint. For example, how can we reorganize a project, idea or a product to make it more efficient?
Why should you use the S.C.A.M.P.E.R. technique?
The S.C.A.M.P.E.R. technique is a helpful tool for coming up with new ideas and solutions by approaching a problem or challenge from various angles and perspectives. Teams can come up with fresh and unique solutions to complex problems.
Technique #17: Forced connections
Forced connections is a creative technique that involves creating random associations between seemingly unrelated ideas or concepts.
The goal of this technique is to encourage groups to think outside of their usual thought patterns and to make new, unexpected connections between ideas.
Here are some steps you can take to hold a successful forced connections brainstorming session in your team:
- Identify the topic or problem — make sure it is clearly defined and all participants understand it.
- Generate a list of random, unrelated concepts or objects. You can use cards with pictures or words, or have participants suggest ideas. For example, you might have a card with a picture of a watch, a card with the word “technology,” and a card with a picture of an mp3 player.
- Assign each participant a random concept or object. They should not share their assigned concept with the group yet.
- Set a time limit, such as 15 minutes, and ask participants to brainstorm ways their assigned concept or object could be related to the topic. Give them a specific number of ideas to come up with — for example 10 different ideas.
- When the timer goes off, ask participants to share their thoughts with the group. Encourage them to explain how they linked their concept or object to the topic or problem.
- Repeat the process several times, assigning different concepts or objects to each participant each time.
- After that, ask participants to go over the ideas that were generated and identify any that could be developed further or combined with other ideas to create even more innovative solutions.
Using this technique, people created some of the modern gadgets that we use every day. They combined a phone, camera, calculator, computer, mp3 player, and many more ideas into one and created a smartphone.
Why should you use the forced connections technique?
The forced connections technique is a great and fun way to think outside of the box and create unique ideas. It is especially useful for groups because team members can build on each other’s ideas and combine individual ideas into a single one.
Whether you’re working on a creative project, dealing with a difficult problem, or simply looking for new ways to think about a familiar subject, the forced connections technique can help you break out of old patterns and stimulate new perspectives.
Brainstorming tips by experts
We have contacted experts who had experience with brainstorming techniques and asked them to give us some useful tips on how to conduct an effective and productive brainstorming session. Here is what they had to say.
Tip #1: Use visual aids
According to Sven Patzer, the Chief Executive Officer of Sveny Corporation, visual aids help when organizing a brainstorming session:

”Visual aids like mind maps, whiteboards, and sticky notes can help to organize and clarify ideas, and can also spark new insights and connections.”
Including some color and casualness into these brainstorms will cause them to be more fruitful.
Tip #2: Use tools to make your brainstorming sessions interactive
Another expert who shared his brainstorming ideas with us is Jarir Mallah, an HR Specialist at Ling App:

“Using tools like Google Jamboard or Miro can increase interaction and engagement. Each tool allows for independent participation in a group atmosphere. The tools can be used remotely which is also a bonus allowing for collaboration from anywhere in the world.”
Miro and Jamboard are two interactive whiteboards designed specifically for team collaboration. These tools will make your brainstorming sessions more productive and enjoyable.
💡Clockify Pro Tip
If you are managing a large team and you want to know how to track your team’s productivity, read the following blog post:
Tip #3: Define the topic or idea that you’re generating
The VP of Communications at CEDIA, Christine DeJoy, shares tips and methods she implements in her marketing and communications team.

“Make sure your team knows what needs to be solved or created before you jump into the fun part, brainstorming!”
So, before you begin brainstorming, clearly present:
- The topic,
- Problem, or
- Type of ideas that team members should generate.
Tip #4: Make sure that your team knows that they are in a creative safe space
Another tip that Christine DeJoy shared with us is that your team members need to know that they can express their ideas without fear of being judged.

“That means that any idea is a good idea, and there should never be any hesitation to share something you find thought-provoking or interesting at any level. Since my team focuses on marketing and coming up with new and creative ideas regularly, I hold a ‘Now Trending…’ meeting monthly. We review what we’ve all come across on social, in media, digitally, and even hard copy assets. We look at what works, why they resonated with us, and then discuss what we can take from those learnings and apply to our target audiences.”
Tip #5: Start out with one-to-ones
A Creative Director at Imagefix, Garry West, shared his thoughts with us.

“Some people won’t open their mouths in a group, but they’re happy to talk to one person. Give pairs 5 minutes to come up with some initial ideas.”
These one-on-one discussions are important because some people feel more comfortable talking to just one person. It also makes sure that all the participants contribute to the brainstorming session.
Tip #6: Take breaks in between brainstorming sessions
We also asked Nina Predojevic, a Social Media Specialist at Cake.com, to share her number one brainstorming tip with us. She says:

“Taking short breaks in between brainstorming sessions can help refresh your mind and allow you to come back to the task with a greater level of creativity. Breaks allow you to step away from the task and give your mind a chance to rest and recharge. For example, you could take a short walk outside, grab a snack or coffee, listen to music, meditate, or do a few stretches.”
Breaks can also help you to relieve stress and anxiety and clear your mind. After a short break, you will have clearer thoughts and will be able to focus better on the task at hand.
💡Clockify Pro Tip
Staying concentrated at work can be challenging sometimes, so if you want to know how to be more focused at work, read the following blog post:
Benefits of team brainstorming
Brainstorming is a creative group activity and it comes with a lot of benefits. The following are some of the most common ones.
Benefit #1: Brainstorming generates a large number of ideas
The well-known benefit of group brainstorming is creating a lot of new ideas. Brainstorming encourages all participants to openly express their thoughts and ideas.
This can be extremely helpful when trying to come up with new ideas for a problem you are too familiar with. In that case, you can’t look at it objectively, so you simply don’t see any other possibilities. Consequently, receiving unbiased feedback from others can provide you with a fresh perspective.
Since there are more participants (your team members), you get more ideas. As a result, you are more likely to stumble upon a brilliant idea.
Benefit #2: Brainstorming sparks creativity and innovation
Brainstorming is a powerful tool for fostering creativity and innovation. A brainstorming session allows participants to share their unique perspectives and build on the ideas of others.
By creating a non-judgmental atmosphere, team members can feel safe to share their most unconventional and creative ideas without fear of criticism. Brainstorming brings people from various backgrounds together, which can result in a broader range of ideas and perspectives.
Group brainstorming also encourages experimentation with various ideas and brainstorming techniques, allowing you to generate ideas you would not have considered otherwise.
Benefit #3: Builds teamwork and collaboration
One of the greatest benefits that brainstorming brings to teams is that it promotes team spirit and team collaboration.
When team members work together to solve a problem they build stronger relationships. Brainstorming sessions ensure that all participants are on the same page and encourage open communication. This leads to increased employee productivity and company’s success.
💡Clockify Pro Tip
If you are a team leader and you want to learn more about how to create teamwork in the workplace, read our blog post:
Benefit #4: Improves problem-solving skills
Brainstorming can be effective when dealing with complex problems.
It invites input from different people because a new perspective can give our own brains a nudge. This allows us to see the same problem or information in a different light, which improves our problem-solving abilities.
Conclusion: Come up with innovative ideas with the best brainstorming technique for your team
Brainstorming in teams can be an extremely effective tool, not only for problem solving, but for improving upon existing ideas. It is an effective way of boosting your critical thinking and fostering collaboration among team members. Opposing arguments and new perspectives significantly improve your own problem-solving process.
However, larger groups, unbalanced personalities, and improperly moderated sessions also pose risks. To get the most out of your brainstorming sessions, work on finding the technique that is best for your project needs, the size of your team, and the type of people involved.
Also, you can schedule your next brainstorming session with a time tracker like Clockify. That way, you can put a finger on how much time you need to come up with a great idea.



