How many work hours are in a year?
The answer to this question may sound simple at first — full-time employees work 2,080 hours per calendar year. However, it’s a bit tricky to give a clear-cut answer in practice.
Another question may also come to mind, such as why calculate yearly work hours. Well, knowing how many hours you spend at work per year helps you better understand your earnings, among other reasons.
In this guide, we’ll help you calculate how many working hours are in 2025, list the biggest benefits of calculating annual work hours, and more.
Let’s jump right into it.

How many working hours are in a year?
Broadly speaking, there are 2,080 working hours per year — that’s 40 hours of work per week.
The calculation goes as follows:
40 work hours per week (which is the standard in the US) x 52 (the number of weeks per calendar year) = 2,080 work hours a year
The standard 2,080 work hours per year may fluctuate depending on whether it’s a leap year or not. In that case, there can be up to 2,096 working hours (260 to 262 work days in a year).
Track work hours with Clockify
Also, various other factors may impact the calculation of your annual work hours, including your work schedule, time off, holidays, and overtime.
Read on to find out how many work hours are in a year based on different work schedules.
How many work hours in a year (based on your workweek)?
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) doesn’t define the exact number of work hours a full-time or part-time employee must clock in, as it’s solely established by the employer. Therefore, certain workers may work more or less than the standard 40-hour workweek and still be covered by the FLSA.
If you don’t work a traditional 40-hour workweek (2,080 work hours/year), you can use the table below to determine your total annual work hours based on various non-traditional work schedules:
| Work hours per week | Calculation (work hours per week x 52 weeks per year) | Total work hours per year |
| 20 | 20 x 52 | 1,040 |
| 25 | 25 x 52 | 1,300 |
| 30 | 30 x 52 | 1,560 |
| 35 | 35 x 52 | 1,820 |
| 37.5 | 37.5 x 52 | 1,950 |
| 45 | 45 x 52 | 2,340 |
| 50 | 50 x 52 | 2,600 |
| 55 | 55 x 52 | 2,860 |
| 60 | 60 x 52 | 3,120 |
| 65 | 65 x 52 | 3,380 |
| 70 | 70 x 52 | 3,640 |
| 75 | 75 x 52 | 3,900 |
| 80 | 80 x 52 | 4,160 |
Note: These figures don’t account for time off or holidays. Also, you may work more than 80 hours per week. The number of weekly work hours varies depending on the employer and state.
Now you know your total annual work hours, based on your workweek. Next, let’s see how many hours you don’t work in a year, referring to the same work schedules mentioned in this section.
How many non-work hours in a year (based on your workweek)?
To determine how many non-work hours are in a year, subtract total annual work hours based on your workweek from the total hours per year (there are 8,760 hours per calendar year).
The formula for calculating annual non-work hours goes like this:
8,760 hours per calendar year – Total annual work hours (based on a specific workweek) = Total non-work hours per year
Here are the calculations for annual non-working hours based on work schedules from the previous section:
- 20-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 1,040 work hours/year = 7,720 non-work hours/year
- 25-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 1,300 work hours/year = 7,460 non-work hours/year
- 30-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 1,560 work hours/year = 7,200 non-work hours/year
- 35-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 1,820 work hours/year = 6,940 non-work hours/year
- 37.5-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 1,950 work hours/year = 6,810 non-work hours/year
- 40-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 2,080 work hours/year = 6,680 non-work hours/year
- 45-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 2,340 work hours/year = 6,420 non-work hours/year
- 50-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 2,600 work hours/year = 6,160 non-work hours/year
- 55-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 2,860 work hours/year = 5,900 non-work hours/year
- 60-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 3,120 work hours/year = 5,640 non-work hours/year
- 65-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 3,380 work hours/year = 5,380 non-work hours/year
- 70-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 3,640 work hours/year = 5,120 non-work hours/year
- 75-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 3,900 work hours/year = 4,860 non-work hours/year
- 80-hour workweek: 8,760 hours/year – 4,160 work hours/year = 4,600 non-work hours/year
Note: These figures don’t take into account holidays or paid time off. Also, you may work more than an 80-hour workweek. Therefore, you may have less than 4,600 non-work hours per year.
Knowing the number of your non-working hours can aid in planning free time or vacation, and serve as a reference to ensure you maintain a good work-life balance.
Work hours vs. non-work hours
Work hours refer to the time spent performing employment-related activities. In contrast, non-work hours are typically dedicated to rest, hobbies, or other non-work-related activities.

Also, short rest periods, like coffee or snack breaks, are considered compensable work time when offered by the employer. On the other hand, bona fide meal periods aren’t considered work time and are generally not paid (unless regulated by state laws).
Comparing your work time to the time you spend not working can help you identify burnout risks, enhance productivity, and set clear boundaries between work and personal life.
For easier comparison, calculate the percentage of the year you spend working by using the formula below:
(Total work hours per year based on your work schedule / 8,760 hours in a calendar year) x 100 = The percentage of the year spent working
Supposing you work 2,080 hours per year (or 40 hours per week), the percentage of the year you spend at work will be calculated as follows:
(2,080 work hours per year / 8,760 hours in a calendar year) x 100 = 23.7% of the year spent working
So, if you work a standard 40-hour workweek, you’ll spend 23.7% of the year working, not counting any time off or holidays. This also means you’ll spend 76.3% of the year not working, representing the larger portion of the year.
Full-time vs. part-time work hours
As statistics say, about 133 million Americans worked full-time in 2024. Conversely, nearly 28 million Americans worked part-time in the same year. Although the number of part-time employees has increased compared to 2023, the number of full-time workers remains significantly higher.
The reasons for working part-time and full-time also differ. Some employees prefer working part-time as it allows them more flexibility to pursue commitments outside of work, like further education or hobbies. On the other hand, people who seek a higher income and more career advancement opportunities choose to work full time.
Also, employees who work full-time hours are more likely to receive certain benefits than part-time workers. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ report, 99% of full-time workers had access to retirement benefits in 2024, compared to 43% of part-time employees.
How do you calculate work hours per year (+ steps)?
To accurately calculate your annual work hours regardless of your work schedule, you must factor in any paid time off you took for the given year, including:
- Vacation days,
- Sick days, and
- Holidays.
Bear in mind that vacation days, sick days, and holidays aren’t fixed amounts and might depend on your company’s policies or even the state you live in.
To properly calculate the total working hours per year, use the formula below:
(Number of working hours per week x 52) – [(PTO days + the number of paid holidays) x the number of working hours per day] = Total working hours in a year
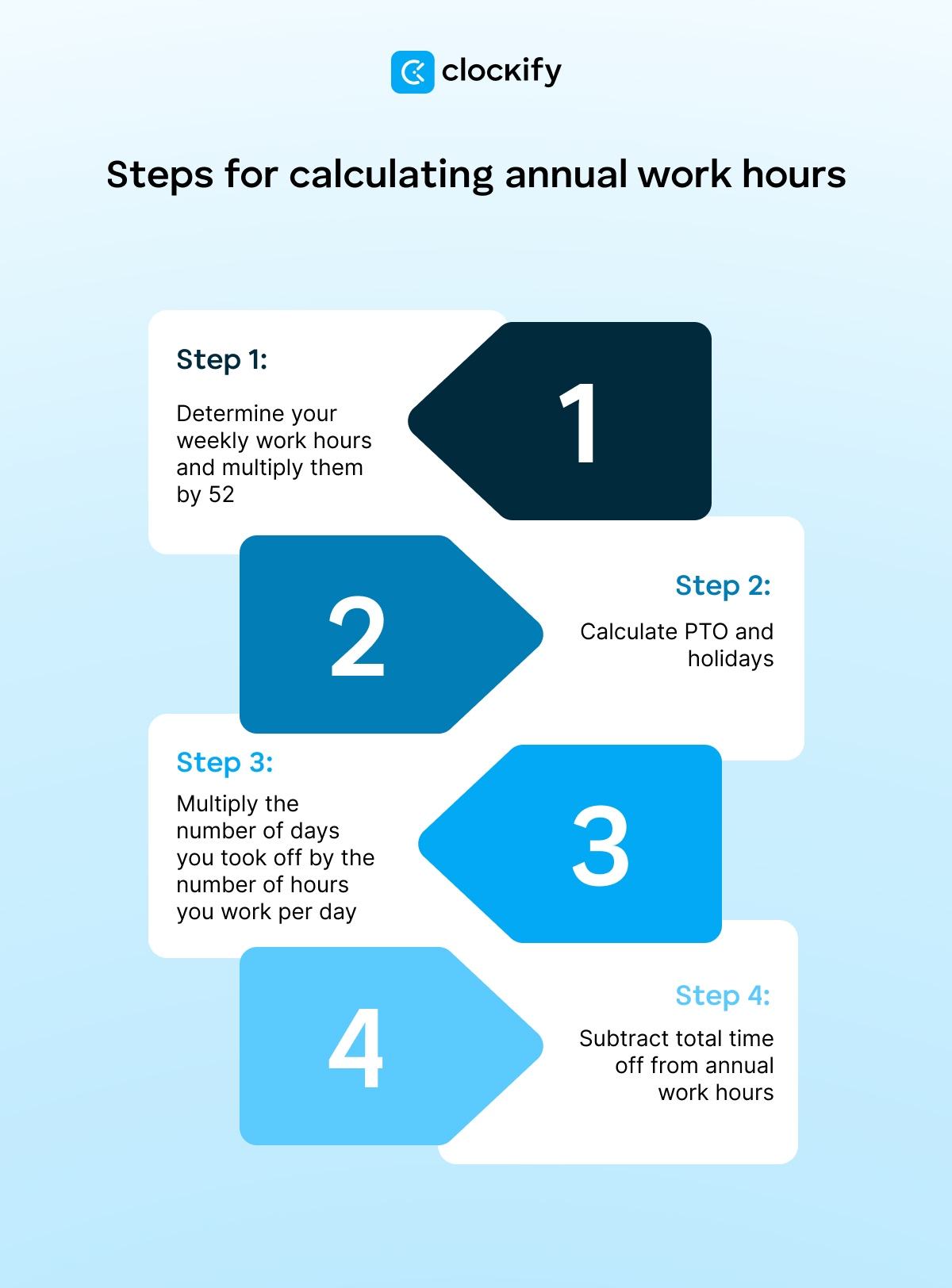
To make sure you get the most accurate calculation of your annual work hours, we’ve broken down the formula into 4 in-depth steps for better understanding.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
If you want to learn more about PTO, holiday, and other employee leave types in different states across the US, check out the resource below:
Step #1: Determine your weekly work hours and multiply them by 52
To calculate your weekly work hours, multiply the hours worked per day by the number of working days for that given week. To streamline the process, you can make use of Clockify’s automatic time card calculator.
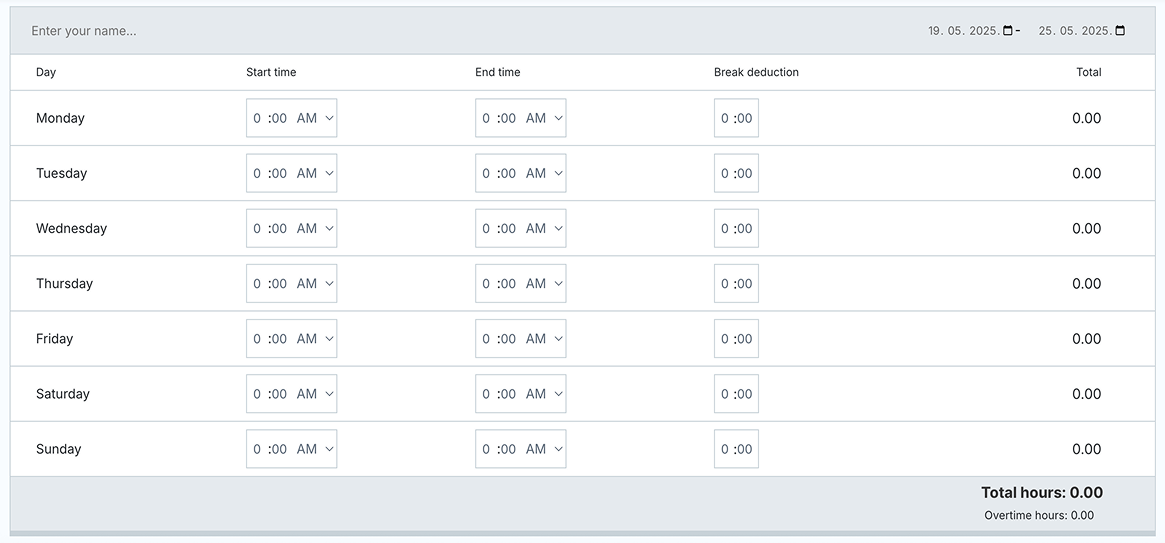
Clockify’s time card calculator records the start and end times of your work day, calculates your overtime for each day, and lunch break periods (which are deducted from the work hours automatically), too.
Let’s say you’ve tracked 35 hours of weekly work (including overtime). Now that you have the number of hours worked per week, multiply it by 52 (the number of weeks per calendar year), as shown below:
35 hours of work per week x 52 = 1,820 working hours per year
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Interested in learning the difference between overtime and double time? Check out the blog post below:
Step #2: Calculate PTO and holidays
According to the US Department of Labor, no employer is required to provide paid vacation leave, including sick or holiday leave, to their employees.
Also, the number of vacation days varies depending on the length of time spent with the employer at a particular job. In 2024, 30% of private industry workers received 10-14 days of paid vacation after 1 year of service, while 32% of private industry employees got 15-19 days of paid vacation after 10 years of service.
Moreover, the number of paid holidays you get also depends on your employer. However, the US recognizes 11 federal holidays, including:
- New Year’s Day (January 1),
- Birthday of Martin Luther King, Jr. (third Monday in January),
- Washington’s Birthday (third Monday in February),
- Memorial Day (last Monday in May),
- Juneteenth National Independence Day (June 19),
- Independence Day (July 4),
- Labor Day (first Monday in September),
- Columbus Day (second Monday in October),
- Veterans Day (November 11),
- Thanksgiving Day (fourth Thursday in November), and
- Christmas Day (December 25).
In addition, Inauguration Day (January 20) is also a public holiday, but it’s held every 4 years and considered a paid holiday for federal employees living in the Washington, D.C. area only.
For easier PTO recording, employers can use Clockify’s PTO and vacation tracker to create various time off policies, including vacation and holiday.
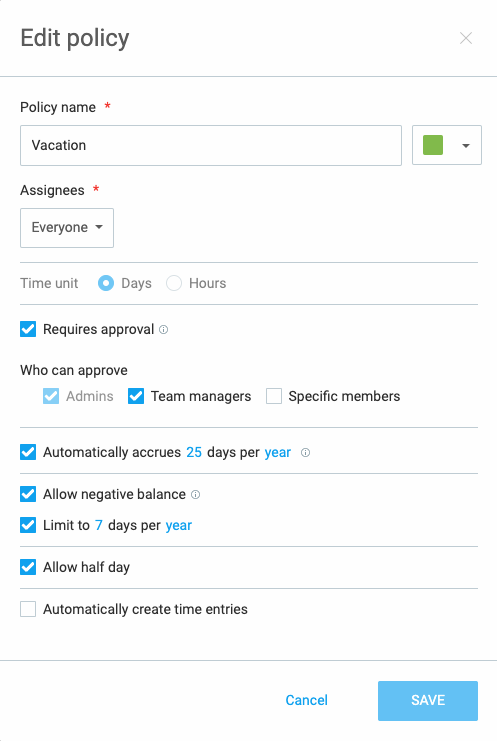
To proceed with your annual work hours calculation, add up all the PTO days you took, including holidays, and prepare for the next step in your calculation.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
To see the latest statistics on PTO in the US, as well as how the US PTO usage and access compare to other countries, read the article below:
Step #3: Multiply the number of days you took off by the number of hours you work per day
If you spent 8 hours a day (no overtime) at your job and had 9 days of vacation that same year, you had a total of 72 hours of vacation time.
Say you also had 11 paid holidays in that certain year and, again, worked 8 hours a day — you had a total of 88 hours of holiday time.
The calculation for the total number of hours you took off from work (including vacation and holiday time) goes as follows:
72 hours of vacation + 88 hours of holiday = 160 PTO hours a year
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Want to learn the difference between PTO, vacation, and sick time? Read the following blog post:
Step #4: Subtract total time off from annual work hours
Now that you have all the numbers you need, subtract the number of hours you didn’t work for that year (160) from the total number of hours worked (1,820), like in the following equation:
1,820 – 160 = 1,660 total work hours per year
Finally, your total annual work hours equal 1,660.
Why is it important to calculate how many hours you work in a year?
Figuring out how many hours you spend at work in a year has many benefits. One is that it allows you to create a healthy work-life balance, which will help you prosper both on and off the clock.
Take a look at the other benefits of calculating your total working hours per year in the section below.
Benefit #1: Calculating work hours helps you estimate your annual income
If you’re an hourly employee, calculating your annual work hours can help you determine your annual salary. This information lets you create a budget plan, set savings goals, and manage your debts.
Whether you want to get valuable insight into your earnings or invest in a new business venture, calculating the hours you spend at your job is the path to successful financial planning.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Make use of the following step-by-step guide to calculate your work hours and your payroll trouble-free:
Benefit #2: Calculating work hours helps you maintain a quality work-life balance
According to Gallup’s 2025 World Happiness Report, Finland, Denmark, and Iceland occupy the first 3 spots on this list. One of the main reasons for their happiness is that they boast a healthy work-life balance, thanks to their generous vacation and parental leave policies.
Compared to nearly two-thirds of Americans who don’t even use all of their vacation days, the Scandinavians can serve as a great example of the importance of having a proper professional-personal balance.
Being aware of how many work hours you clock in, stopping yourself from overworking, and using your PTO regularly leads to an optimal quality of life.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
If you’re looking to shorten your workweek, here’s an interesting blog post for you:
Benefit #3: Calculating work hours helps you estimate your hourly rate
If you’re paid a fixed salary rather than by the hour, you may want to know how much money you earn per hour. You can easily determine your hourly rate by dividing your annual income by the number of hours worked per year.
So, for instance, if you’ve worked 2,080 hours in a previous year, and your annual salary for that year was $45,000, your hourly rate is calculated as follows:
$45,000 / 2,080 = $21,6 per hour
Being mindful of their annual work hours, salaried employees can more easily determine their hourly wage.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
Which one is better for you, a salary or hourly employment? If you still can’t decide but you’re thinking about changing your career, maybe the following blog post will help you out:
Benefit #4: Calculating work hours helps employers abide by labor regulations
As an employer, fulfilling your legal responsibilities towards your employees is crucial. Keeping an accurate track of your employees’ work hours per year will help you do the following:
- Compensate your employees appropriately (whether that’s regular or overtime hours, bonuses, or commissions),
- Give promised benefits (PTO, retirement plan, etc.),
- Determine labor costs,
- Differ between part-time and full-time employees, and
- Provide employees with a harmonious life.
By keeping a thorough record of your employees’ annual work hours, you avoid making wage and hour violations that may result in monetary penalties.
Record work hours with Clockify
Benefit #5: Calculating work hours makes a great ally to the HR department
It’s old news that the HR sector deeply relies on the calculation of working hours for multiple reasons, including:
- Determining wages/salaries,
- Accounting for time off,
- Differentiating between full-time and part-time workers, and others.
To perform the necessary calculations, HR managers can use manual timekeeping methods, such as paper timesheets or spreadsheets, to record employee work hours.
However, tracking employee hours via these outdated methods is time-consuming. Not to mention all the extra hours HR managers will have to spend trying to decipher or fix inaccurate time logs.
With a reliable time tracking tool such as Clockify, you can accurately track employee work hours and run detailed reports of employees’ tracked time for further analysis. Just select the desired time range and filter the report for more precise information. In fact, the tool automatically calculates pay (or cost) based on the employee’s hourly rate.
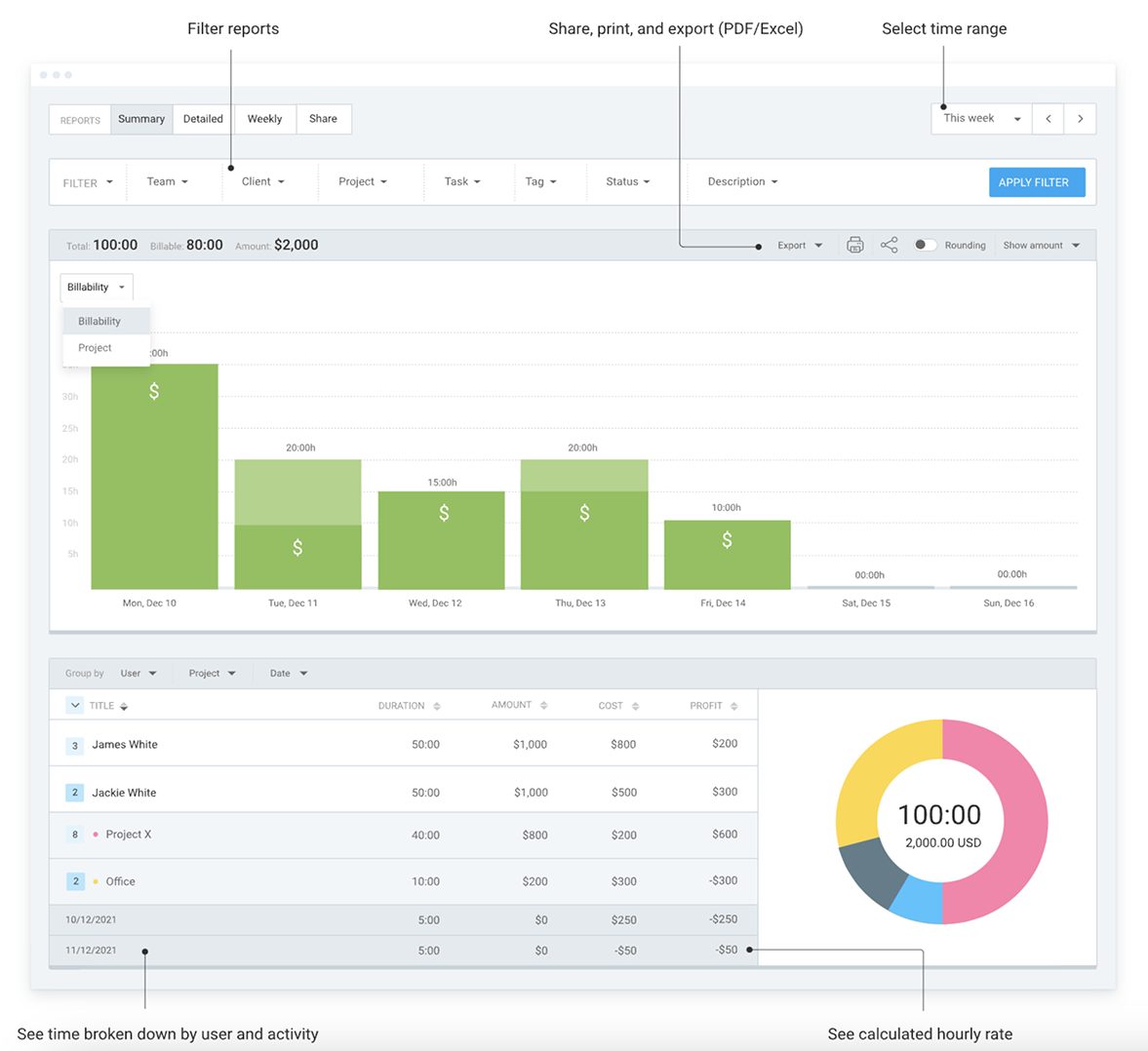
Recorded work hours later help HR specialists automate payroll, invoice clients, create PTO policies, manage employee scheduling, and much more.
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
To learn more about how Clockify can assist with HR automation and improve HR efficiency, take a look at the following blog post:
FAQs on work hours
Get answers to some frequently asked questions about working hours in the following section.
How many hours are in a 40-hour work year?
If you work a 40-hour workweek and have the same work schedule all year long, you’ll spend 2,080 hours at work that year (not including any time off or holidays).
How many hours does a full-time employee work in a year?
How many hours you’ll work in a year as a full-time employee depends on the number of hours you work per week.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) sets guidelines for full-time employees of at least 30 hours per week. While this is the minimum number of hours an employee has to work to be considered a full-time employee, full-time workers typically work 35-40 hours per week.
Say you work 37.5 hours a week for the entire calendar year. In this case, your full-time working hours per year equal 1,950 (not counting time off and federal holidays).
How many hours does a part-time employee work in a year?
Similarly to full-time employees, how many hours you’ll work in a year as a part-time worker depends on your work schedule. As a general guideline, part-time employees typically work between 20 and 29 hours per week.
For example, if you work 25 hours per week for all 52 weeks of the year, you’ll spend 1,300 hours at your job in a year.
Do 2,080 hours per year include holidays?
No, 2,080 work hours per year don’t include holidays because the FLSA doesn’t require employers to give time off for holidays, vacations, or sick leave.
How many Americans work more than 40 hours a week?
As per the Kickresume’s survey from 2024, more than 40% of American respondents said they work 41 to 50 hours per week, while 8% of Americans reported working more than 51 hours a week.
Moreover, according to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), nearly 15 million Americans work irregular shifts, including extended, rotating, and consecutive shifts, which often result in more than 40 hours of work per week.
What are the average monthly working hours?
The number of working hours in a month typically ranges from 160 to 184 hours, depending on the number of working days in a particular month.
For instance, in February, which has 20 working days in a regular year (21 working days in a leap year, if the extra day falls on a workday), there are 160 work hours (assuming you work 8 hours a day).
To see how we got this number, look at the calculation below:
20 working days in February x 8 work hours per day = 160 work hours in February
💡 CLOCKIFY PRO TIP
For more interesting statistics about average working hours, make sure you check out the resource below:
What are the average work hours in a quarter?
A quarter is typically 3 months, with an average of 4 workweeks per month. The number of workweeks per month can vary because some months are shorter than others.
To determine your work hours in a quarter, you need to multiply your work hours per week by 12 (the number of working weeks per quarter). If you work 40 hours per week, the calculation for your quarterly work hours goes as follows:
40 hours per week x 12 = 480 work hours per quarter
Remember that this figure is based on an average of 4 workweeks per month. It also doesn’t include vacations and federal holidays.
Use Clockify to never forget to track your work hours again
Whatever your work hours or work schedule, chances are you sometimes forget to clock in what you were up to.
Those days are gone.
Now, you can use a powerful time tracking tool, such as Clockify, and make your life easier with automatic timesheet reminders.
To set reminders in Clockify, you need to:
- Specify the target number of hours per day, week, or month,
- Define when you want Clockify to send out the reminders, and
- Choose who you want to send the reminders to.
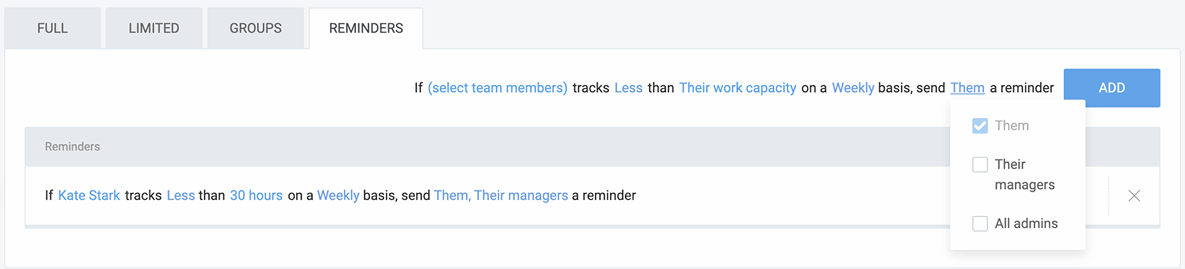
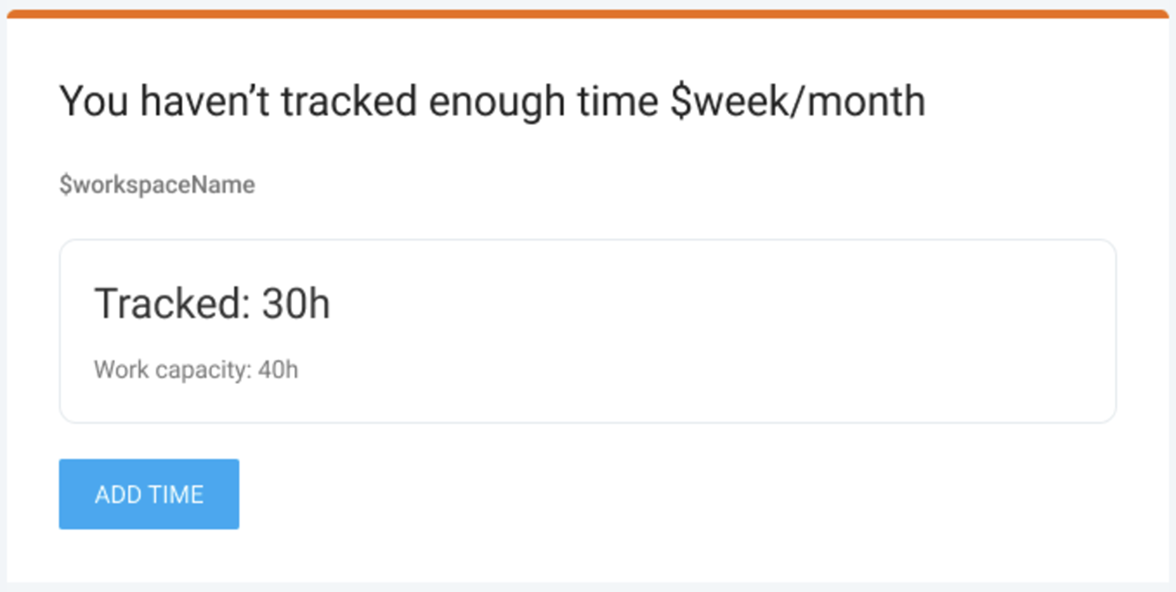
As soon as you set the reminder up, you’ll never again fail to log your work hours. And here’s the message you get when you forget to track enough time:
Apart from the timesheet reminders, you can set You forgot to start the timer reminders in Clockify. That way, you’ll get a message each time you forget to start the timer at a specific time. Just choose your working days, working hours, and after how much time you wish to be reminded, as shown below:
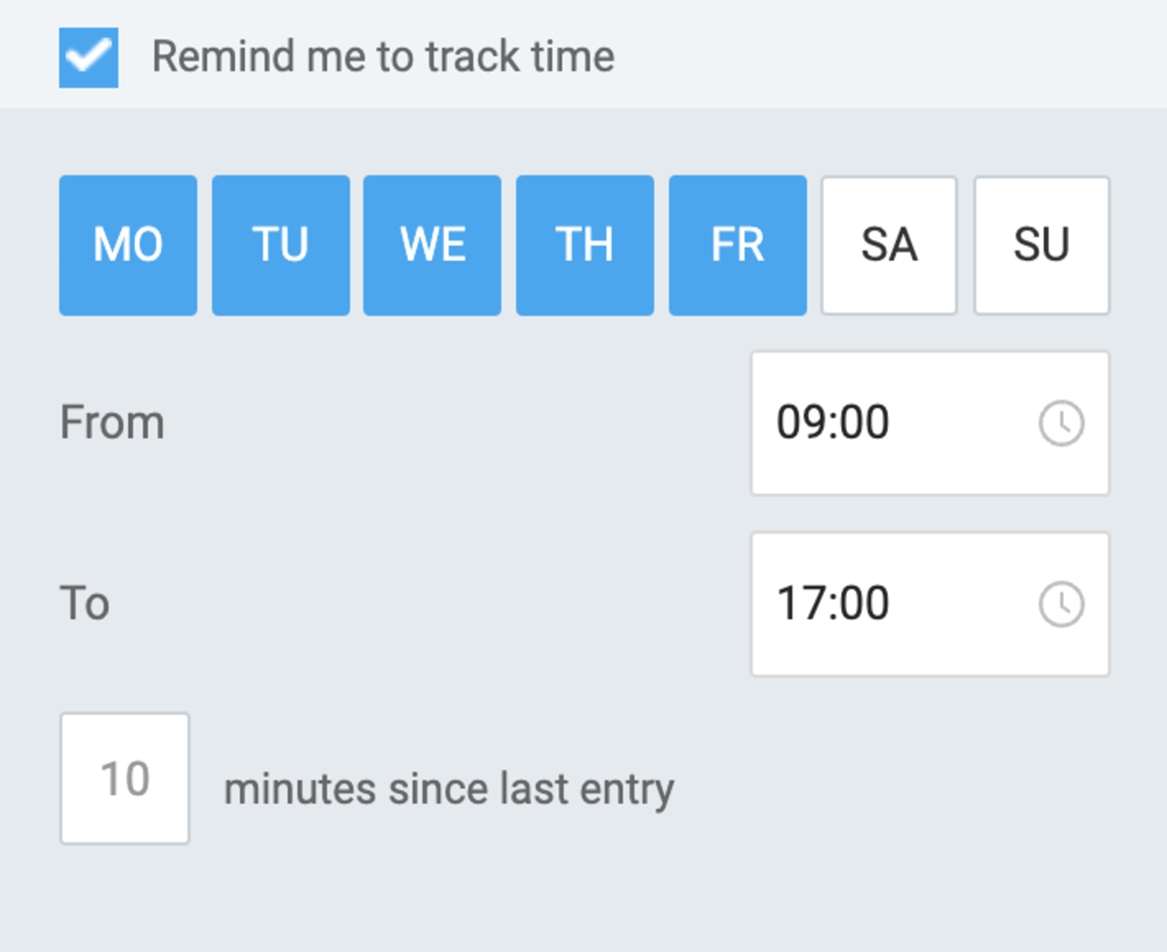
For example, say you want to start working every morning at 9 a.m. Yet, you often forget to start your timer, leading to timesheet issues. With the You forgot to start the timer reminder, you can make fewer mistakes and have accounting look more kindly upon you.



