Employing minors is quite delicate, and employers who decide to employ workers under the age of 18 must respect child labor laws to avoid fines and penalties.
Both federal and state laws regulate child labor, and these laws help ensure that minors work in fair conditions and are compensated properly.
Navigating state and federal labor laws about child employment can be demanding, which is why in our guide, we’ll help you understand the employment restrictions concerning:
- Every state’s minimum legal working age,
- Work hours regulations for minors,
- Hazardous occupations prohibited to children of different age, and
- Required documentation for youth employment.
Knowing these working standards and requirements regarding child labor in the US will keep you compliant with state and federal laws and help you avoid paying hefty fines and civil penalties.
*Note: The information regarding minimum working age laws and regulations by state has been checked and updated for 2025.

- Federal law states that the minimum working age for minors in non-agricultural jobs is 14.
- According to federal law, the minimum working age for minors is 12 in agricultural jobs.
- Depending on their age category, minors have limits on how many work hours they can have in a day.
- Many US states have their own laws regarding the minimum working age for minors in agricultural and non-agricultural jobs.
Federal regulations for youth employment
On the federal level, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) sets the conditions under which employers can employ children.
The act regulates different aspects of child labor, such as:
- Working age requirements,
- Working hour restrictions,
- Occupational restrictions, and others.
Due to many states having their own laws regarding child labor, federal and state regulations can be different. In situations like these, the provisions of the more restrictive law will apply.
Federal age requirements for employment of minors in non-agricultural jobs
Federal law mandates the following age requirements for minors working in non-agricultural jobs. Here is a breakdown:

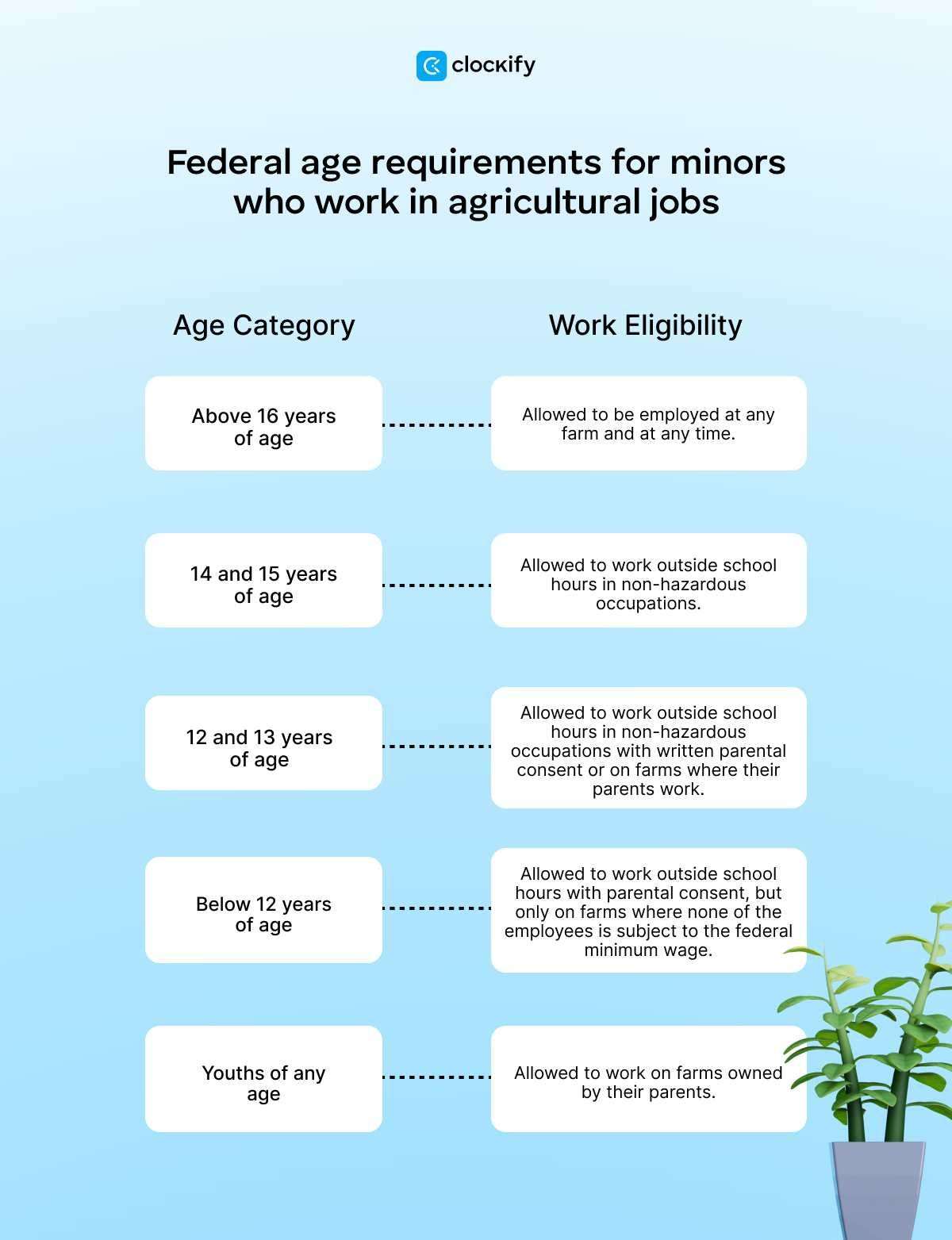
Federal age requirements for employment of minors in agricultural jobs
On the other hand, the age requirements for minors working in agricultural jobs are the following:
Federal working hours restrictions for minors in non-agricultural jobs
In addition to the minimum working age requirements, the federal law also limits the number of working hours for youth workers in non-agricultural occupations.
The FLSA states that minors 18 years of age and older may work unlimited hours in any job, regardless of whether it’s considered hazardous.
On the other hand, minors aged 16 and 17 may only work for unlimited hours in non-hazardous occupations.
When it comes to minors aged 14 and 15, the FLSA prohibits them from working:
- During school hours,
- More than 3 hours on a school day,
- More than 8 hours on a nonschool day,
- More than 18 hours per week when school is in session,
- More than 40 hours per week when school isn’t in session, and
- Before 7 a.m. and after 7 p.m. (except between June 1 and Labor Day — no work after 9 p.m.).
Federal occupational restrictions for all minors in non-agricultural jobs
Certain jobs can be dangerous and detrimental to the health and well-being of minors. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) defines these occupations as hazardous for minors in non-agricultural fields.
Therefore, minors under the age of 18 aren’t allowed to work in the following occupations:
- Manufacture or storage of explosives,
- Motor-vehicle driving,
- Most coal mining jobs,
- Forest fire fighting, forest fire prevention, timber tract, forestry service, logging, and sawmilling occupations,
- Power-driven woodworking machine operating (e.g., chainsaws, nailing machines, and sanders),
- Occupations involving exposure to radioactive materials and ionizing radiation.
- Operating power-driven hoisting apparatus (e.g., forklifts, non-automatic elevators, skid-steers, skid-steer loaders, etc.),
- Operating power-driven metal-working, punching, and shearing machines (but they are allowed to use most machine tools),
- Most mining jobs other than coal (metal mines, quarries, aggregate mines, underground mines, open cut mines, or open quarries, and sand, or gravel jobs),
- Jobs that include operating power-driven meat processing machines and working in meat and poultry slaughtering and meat-packing (e.g., meat slicers, saws, choppers, etc.),
- Operating power-driven bakery machines, including batter mixers, dough rollers, rounders, dividers, sheeters, and cookie or cracker machines,
- Jobs that involve operating balers, compactors, and power-driven paper-product machines,
- Occupations dealing with the manufacture of brick, tile, and related products,
- Occupations involving the operation of power-driven tools (such as circular saws, band saws, guillotine shears, chain saws, etc.),
- Jobs related to wrecking, demolition, and ship-breaking (except remodeling or repair work),
- Roofing jobs (any type of work on or about a roof), and
- Jobs related to trenching and excavation.
According to the Secretary of Labor, the potential risks associated with these jobs are higher than in other non-agricultural occupations. For this reason, the minimum age requirement is higher.
Minimum working age by state table
Although federal law establishes clear rules regarding child labor, many states have also enacted laws regulating youth employment.
As with the federal rules, state laws regulate:
- Minimum working age,
- Maximum number of work hours, and
- Hazardous occupations for minors.
Let’s explore the minimum working age requirements by state (both agricultural and non-agricultural occupations) in the tables below.
Child labor regulations on agricultural jobs by state
Many US states set their own minimum working age requirements for minors who work in agricultural jobs during school and non-school hours.
In the table below, we cover:
- The minimum age requirements for agricultural jobs,
- The number of hours a minor is allowed to work per day/week, and
- Employment certificate or proof of age requirements.
| State | Minimum working age | How many hours and days can a minor work | Required certificates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alaska | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Up to 9 hours a day and 23 hours per week (work and school hours combined). Up to 6 work days per week for minors under 18. | Employment certificate isn’t required. Age certificate is required for all minors under the age of 18. |
| Arizona | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. | N/A |
| Arkansas | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Minors aged 16: Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week. Minors aged 17: Up to 10 hours per day and 54 hours per week. Up to 6 work days per week for minors under 18. | N/A |
| California | 18 — but minors who aren’t required to go to school can work at 16 during school hours. 12 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Minors aged 12 to 13: Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week on a non-school day/week; up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week on a school day/week. Minors aged 16 and 17: Up to 4 hours on a school day or up to 8 hours on a day that precedes a school day. Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week when school is off. Up to 6 work days for minors. | Employment certificate required for all minors under the age of 18. |
| Colorado | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 12 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Minors under 18: Up to 8 hours per day and up to 40 hours per week. Minors under 16: Up to 6 hours per day on a school day. Minors over 14: Up to 12 work hours in 24 hours and up to 30 in 72 hours. | Age certificate required for all minors under the age of 18. |
| Connecticut | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week. | Employment certificate required as well as a proof of age or an agriculture permit for minors under the age of 16. |
| Delaware | Exempt from farm work except for nonhazardous occupations. | Exempt from farm work except for hazardous occupations. | N/A |
| Florida | 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Minors aged 15: Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week when school isn’t in session; up to 3 hours per day and 15 hours per week when school is in session. Minors aged 16 and 17: Up to 8 hours per day and 30 hours per week (40 for 17-year-olds) during school period. Up to 6 work days per week. | Age certificate required for all minors under the age of 18. |
| Hawaii | 18 — but minors who aren’t required to go to school can work at 16 during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours (15 for pineapple harvesting and 10 for coffee harvesting). | Minors under 14: Up to 6 hours per day and 30 hours per week for no more than 5 consecutive days during non-school period in coffee harvest. Minors aged 14 and 15: Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours a day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week in pineapple harvesting from June 1 through the day before Labor Day. Up to 6 work days per week. | Employment certificate required for minors under the age of 18. Age certificate required for 16- and 17-year-old minors. |
| Idaho | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. | Up to 9 work hours per day and 54 hours per week. | N/A |
| Illinois | 12 — for minors who work during school hours. 10 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | N/A | N/A |
| Indiana | 12 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Minors 14–17 years of age are exempt from the requirements for non-farm work. | As of July 1, 2021, Indiana no longer issues employment or age certifications, instead employers must register all employed minors in an employer registration system maintained by the Indiana Department of Labor. |
| Iowa | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours (12 for migratory labor). Younger minors can work with a permit from the Labor Commissioner upon court order. | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 4 hours per day, 28 hours per week during school period. | Employment certificate required for all minors under the age of 16. |
| Maine | 16 — for minors who work during school hours unless exempt by the school’s director. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours. Minors under this age can work in planting, cultivating, or harvesting, but they can’t be in contact with hazardous machinery or substances. | There are no regulations regarding how many hours and days a minor can work per week. | If not in direct contact with hazardous machinery or substances, minors are exempt from child labor laws. 18-year-olds must provide an employment certificate only if they are in direct contact with hazardous machinery or substances. Age certificate not required. |
| Massachusetts | 14 — for minors who work during school hours with a certification. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours and with a vocational education certificate. | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 4 hours per day and 24 hours per week during school period. | Employment certificate and proof of age is required for all minors under the age of 18. |
| Michigan | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 13 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Minors under 16: Up to 10 hours per day and 48 hours per week. If in school, no more than 48 hours per week (work and school hours combined). Minors Aged 16 to 18: Up to 10 hours per day and 48 hours per week. If in school, a maximum of 24 hours per week. If working in farming: Up to 11 hours per day and 62 hours per week with parental consent, only if the minor isn’t employed between 2 a.m. and 5:30 a.m. Up to 6 work days per week for minors under 18. | Employment certificate and proof of age is required for all minors under the age of 18. |
| Minnesota | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 12 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | There are no regulations regarding how many hours and days a minor can work per week. | Employment certificate is required for all minors under the age of 16 for work during school hours, and proof of age is required for all minors under the age of 18. |
| Missouri | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day during school period. Up to 6 work days per week. | Employment certificate is required for all minors under the age of 16 for work during school term, and proof of age is required for all minors under the age of 18 on request. |
| Nevada | 14 — for minors who work during school hours. | N/A | Agriculture is exempt from Nevada child labor laws, except for minimum age during school period. |
| New Hampshire | 18 — but minors who aren’t required to go to school can work at 16 during school hours. 12 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Up to 8 hours per day during non-school period, 48 hours per week during vacation. Up to 3 hours per day, and 23 hours per week during school period if enrolled in school. Minors aged 16 and 17: Up to 30 hours per week during school and up to 48 hours per week during vacation. Up to 6 work days per week (minors aged 16 and 17 enrolled in school). | N/A |
| New Jersey | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 12 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Up to 10 work hours per day. Up to 6 work days per week. | Employment certificate is required for all minors under the age of 16. |
| New Mexico | 16 — for minors who work during school hours (14 for hardship cases). | Up to 8 hours per day and 44 hours (48 in certain cases for minors under 14) per week. | Employment certificate is required for all minors under the age of 16, and proof of age is required for all minors under the age of 18 (provided on request). |
| New York | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours (12 for harvesting berries, fruits, and vegetables). | Up to 4 work hours per day for minors aged 12 and 13. | Employment certificate is required for all minors under the age of 16. |
| North Dakota | 14 — for minors who work during school hours. | There are no regulations regarding how many hours and days a minor can work per week. | N/A |
| Ohio | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. | 18-year-old minors must provide an employment certificate if residing in an agriculture labor camp. |
| Oregon | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 12 — for minors who work during school hours (9 for picking berries and beans with parental permission). | Up to 10 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period (special permit required for more than 10 hours per day). Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 work days per week. | Employment certificate is required only for minors under 18 who are in direct contact with power-driven farm machinery. |
| Pennsylvania | Farm workers under 14 aren’t allowed to work. | Minors under 18 can’t work from 7 a.m. to 1 hour after the end of the school day. | N/A |
| South Carolina | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours (12 with parental approval). | N/A | N/A |
| South Dakota | N/A | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 4 hours per day and 20 hours per week during school period. | N/A |
| Utah | There is no minimum age limit for minors with parental consent. | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period (unless waived with parental consent). | Proof of age is required for all minors under the age of 18 (on request). |
| Vermont | 16 — for minors who work during school hours (14 with a labor certificate). | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week. | Employment certificate is required for all minors under the age of 16 during school hours. |
| Virginia | 16 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours (12 with parental approval). | N/A | Proof of age is required for all minors under the age of 18 (on request). |
| Washington | 18 — for minors who work during school hours. 14 — for minors who work outside of school hours (12 for hand-harvesting or cultivating berries, cucumbers, and spinach). | Minors aged 12 and 13: Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week when school isn’t in session. Minors aged 14 and 15: Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week when school isn’t in session. Minors aged 16 and 17: Up to 10 hours per day and 50 hours weekly (60 hours for wheat, hay, and pea harvesting) when school isn’t in session. Up to 4 hours per day and 28 per week during school. Up to 6 work days per week (or 7 in dairy, livestock, hay, and irrigation, with one day off every two weeks, under 18). | N/A |
| Wisconsin | 18 — for minors who work during school hours. 12 — for minors who work outside of school hours. | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 per week during school period. During peak seasons, minors 14 to 17 may work outside school hours beyond the permitted weekly hours. After 50 hours a week, minors must be paid overtime (1.5 times the regular hourly wage). Up to 6 work days per week. | N/A |
Although many states allow agricultural work for minors, there are currently 17 states that exempt minors from agricultural employment, including:
- Alabama,
- Delaware,
- Georgia,
- Kansas,
- Kentucky,
- Louisiana,
- Maryland,
- Mississippi,
- Montana,
- Nebraska,
- North Carolina,
- Oklahoma,
- Rhode Island,
- Tennessee,
- Texas,
- West Virginia, and
- Wyoming.
In these states, minors aren’t allowed to work in agriculture.
Child labor regulations on non-agricultural jobs by state
For non-agricultural jobs, the federal minimum age for employment is 14. In non-agricultural employment, minors also have restrictions on the types of jobs they can work and the number of hours permitted.
For example, 14-year-old minors can only work in specific occupations that aren’t considered hazardous to their health and well-being. Moreover, 14- and 15-year-olds are prohibited from working during school hours, while 16- and 17-year-olds can work unlimited hours only in non-hazardous jobs.
In non-agricultural jobs, the federal hour restrictions for minors aged 14 and 15 are:
- Up to 8 work hours on a non-school day,
- Up to 40 work hours in a non-school week,
- Up to 3 work hours on a school day,
- Up to 18 work hours in a school week, and
- No work before 7:00 a.m. or after 7:00 p.m., except from June 1 through Labor Day, when nighttime is extended to 9:00 p.m.
In addition to federal regulations, each state has its rules regarding working hours for non-agricultural workers under 16 and 17 years of age. Let’s look at them in the table below:
| State | Maximum number of work hours and days for minors under 16 | Maximum number of work hours and days for minors aged 16 and 17 | Nightwork |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. during summer vacation) to 7 a.m.16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 10 p.m. before the school day to 5 a.m., if enrolled in school (for the age of 19). |
| Alaska | Up to 9 hours per day and 23 hours per week (work and school hours combined). Up to 6 days per week during school weeks. | Up to 6 days per week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 9 p.m. to 5 a.m. |
| Arizona | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 9:30 p.m. (11 p.m. before non-school day) to 6 a.m.; 7 p.m. to 6 a.m. in door-to-door sales or deliveries. |
| Arkansas | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week. Up to 6 days per week. | 16-year-olds can’t work in excess of 10 consecutive hours or beyond 10 hours in a 24-hour period. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. before non-school day) to 6 a.m. 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 11 p.m. to 6 a.m. prior to the school day. |
| California | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 4 hours per day and 28 hours per week during school period (work and school hours combined). 8 hours on any day preceding a non-school day. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m.16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 10 p.m. (12:30 a.m. before non-school day) to 5 a.m. |
| Colorado | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 9:30 p.m. to 5 a.m. prior to the school day. |
| Connecticut | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week in commerce jobs when the child is on school vacation that lasts more than 5 days. Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week if enrolled in a secondary education during non-school period. Up to 6 hours per day and 32 hours per week during school period in restaurant, recreational, amusement, theater, manufacturing, mechanical, retail, hairdressing, bowling alley, pool hall, or photography gallery businesses. Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week if not enrolled in secondary education in retail stores. Up to 8 hours per day and 49 hours per week in restaurant, manufacturing, mechanical, recreation, amusement, and theater establishments. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. July 1 to the first Monday in September) to 7 a.m.16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 11 p.m. (midnight if school vacation, not prior to a school day, or not attending school) to 6 a.m. in restaurants, recreational, amusement, and theater establishments. 10 p.m. to 6 a.m. in manufacturing, mechanical, and retail establishments (11 p.m. during school vacation, not prior to a school day, or not attending school; midnight in a supermarket of 3,500 ft2 or more when no school the next day). 10 p.m. to 6 a.m. in hairdressing, bowling alley, pool hall, or photography gallery establishments. |
| Delaware | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 4 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 12 hours per day (work and school hours combined). | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work 8 consecutive hours of non-work, and non-school time is required in each 24-hour day. |
| Florida | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 15 per week when followed by a school day (unless enrolled in vocational schools). Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 8 hours per day and 30 hours per week during the school year. Up to 6 days per week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. prior to the school day to 7 a.m. on school day (9 p.m. during holidays and summer vacations to 7 a.m.). 16- and 17-year-olds can’t work from 11 p.m. to 6:30 a.m., prior to the school day. |
| Georgia | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 4 hours per day during school period. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 9 p.m. to 6 a.m. |
| Hawaii | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. to 7 a.m. (9 p.m. to 6 a.m. during authorized school breaks). |
| Idaho | Up to 9 hours per day and 54 hours per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 9 p.m. to 6 a.m. |
| Illinois | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day (8 combined hours of work and school). Up to 24 hours per week during school period. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. |
| Indiana | Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. | If enrolled in school, 16 and 17-year-old minors can work up to 9 hours per day and 40 hours per week in a school week. Up to 48 hours in a non-school week. Up to 6 days per week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t start work before 7:00 a.m. or finish after 7:00 p.m. but may work until 9:00 p.m. from June 1 through Labor Day, except on a night followed by a school day. They can’t work during school hours on a school day, except in certain entertainment jobs;16- and 17-year-old minors may work until 10:00 p.m. on nights followed by a school day (except for hazardous jobs) or until 11:00 p.m. with written parental permission. They can’t work in an establishment that operates between 10:00 p.m. and 6:00 a.m. unless another employee (at least 18 years of age) also works during the same hours. 16- and 17-year-old minors may work adult hours only if they are high school graduates, have completed an approved career and technical education, or aren’t enrolled in a regular school term. |
| Iowa | Up to 6 hours per day and 28 hours per week during school period. Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. |
| Kansas | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work after 10 p.m. prior to the school day to 7 a.m. |
| Kentucky | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. | If enrolled in school, 6 hours per day and 30 hours per week (8 hours on Saturday and Sunday). Up to 40 hours per week with parental consent and at least a 2.0 school grade point average. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m.16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 11 p.m. (1 a.m. Friday and Saturday) to 6 a.m. during school period. |
| Louisiana | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. Non-graduates can’t work from 7 p.m. to 7 a.m. on any school day (9 p.m. to 7 a.m. on any non-school day). Non-graduate 16-year-olds can’t work from 11 p.m. to 5 a.m. before the start of a school day, while non-graduate 17-year-olds can’t work from 12 a.m. to 5 a.m. before a school day. |
| Maine | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week for 6 consecutive days during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week for 6 consecutive days during school period. | If enrolled in school, up to 10 hours per day and 50 hours per week for 6 consecutive days during a non-school week. Up to 6 hours per day and 24 hours per week (except 8 hours on the last scheduled day of school week) for 6 consecutive days during a school week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. during summer vacation) to 7 a.m. If enrolled in school, 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 10:15 p.m. (12 a.m. before non-school day) to 7 a.m. during school period and to 5 a.m. otherwise. |
| Maryland | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 4 hours per day and 23 hours per week during school period. Up to 8 hours on Saturday and Sunday if a minor does not work outside school hours for more than 6 consecutive days a week. The total working hours outside school shouldn’t be more than 24. | Up to 12 hours per day (work and school hours combined). | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 8 p.m. (9 p.m. Memorial Day through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. On a non-school day, 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work more than 8 consecutive hours per day without a break. |
| Massachusetts | Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 8 hours a day on Saturday, Sunday, and holidays. Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 9 hours per day and 48 hours per week, regardless of the school period. Up to 6 days per week. | Minors younger than 16 can only work between 6:30 a.m. and 7 p.m. during the school year and between 6:30 a.m. and 9 p.m. during the summer (from July 1 through Labor Day). 16- and 17-year-old minors can work between 6 a.m. and 10 p.m. (on nights before a regular school day) or between 6 a.m. and 11:30 p.m. (on nights not preceding a regular school day). The exception is in restaurants and racetracks, where they can work between 6 a.m. and 12 midnight (on nights not preceding a regular school day). After 8:00 p.m., all minors must be supervised by an adult unless they work at a kiosk, cart, or stand in a secured shopping mall. |
| Michigan | Up to 10 hours per day and 48 hours per week (work and school hours combined). Up to 8 hours per day during a non-school day. Up to 6 days per week. No work during school hours. | Up to 10 hours per day (work and school hours combined). Up to 24 hours in a school week and 48 hours in a non-school week. Up to 6 days per week. No work during school hours. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 9 p.m. to 7 a.m. If enrolled in school, 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 10:30 p.m. (11:30 p.m. on Fridays, Saturdays, and during school vacations) to 6 a.m. if attending school. If not, from 11:30 p.m. to 6 a.m. |
| Minnesota | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 9 p.m. to 7 a.m. 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 11 p.m. to 5 a.m. before a school day (11:30 p.m. to 4:30 a.m. with written parental consent). |
| Mississippi | Up to 8 hours per day and 44 hours per week in a factory, mill, cannery, or workshop. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. to 6 a.m. in a factory, mill, cannery, or workshop. |
| Missouri | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day when school is in session. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day; 10:30 p.m. at regional Fairs or expositions) to 7 a.m. |
| Montana | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. during non-school period (June 1 through Labor Day, depending on local standards) to 7 a.m. |
| Nebraska | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week. | N/A | Minors under 14 can’t work from 8 p.m. to 6 a.m. 14- and 15-year-old minors can’t work from 10 p.m. (beyond 10 p.m. before a non-school day; they’re only allowed with a special permit) to 6 a.m. |
| Nevada | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week. | N/A | N/A |
| New Hampshire | Up to 8 hours per day during non-school period. Up to 48 hours per week during vacation if enrolled in school. Up to 3 hours per day and 23 hours per week during school period, if enrolled in school. | If enrolled in school, up to 48 hours a week and up to 6 workdays during vacation. If not on vacation, up to 30 hours in a week and up to 6 workdays if enrolled in school. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 9 p.m. to 7 a.m. |
| New Jersey | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 per week. Minors aged 16 and above may work up to 10 hours per day and 50 hours per week only between the last day of school and Labor Day. Up to 6 days per week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. from the last day of school through Labor Day in non-school weeks with written permission) to 7 a.m.16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 11 p.m. to 6 a.m. during school. |
| New Mexico | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. outside the calendar school year) to 7 a.m. |
| New York | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | If enrolled in school, up to 8 hours per day and 48 per week during non-school period (Friday, Saturday, Sunday, holiday). Up to 4 hours per day and 28 hours per week on a day preceding a school day (Monday – Thursday). Up to 6 days per week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 21 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m.16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 10 p.m. (or midnight prior to the school days with written parental and school consent and before non-school days with written parental consent) to 6 a.m. during school days/weeks. Midnight to 6 a.m. outside school days/weeks. |
| North Carolina | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. during summer vacation) to 7 a.m. 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 11 p.m. to 5 a.m. prior to the school day during school (except with written parental and school consent). |
| North Dakota | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period (if not exempted from school attendance). Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. |
| Ohio | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 to Sept. 1 and during school holidays of 5 school days or more) to 7 a.m., 7 p.m. to 7 a.m. in door-to-door sales. 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 11 p.m. prior to the school day to 7 a.m. on school day (6 a.m. if not employed after 8 p.m. the previous night) if attending school; 8 p.m. to 7 a.m. in door-to-door sales. |
| Oklahoma | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. |
| Oregon | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 44 hours per week (emergency overtime with permit). | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. |
| Pennsylvania | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 10 hours per day and 48 per week during non-school period. Up to 8 hours per day and 28 per week during school period. Up to 6 days a week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (10 p.m. during vacation from June to Labor Day) to 7 a.m. If enrolled in school, 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 12 p.m. (1 a.m. before non-school day) to 6 a.m. |
| Rhode Island | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week. | Up to 9 hours per day and 48 hours per week during the school year. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. during school vacation) to 6 a.m.; If regularly enrolled in school, 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 11:30 p.m. (1:30 a.m. before non-school day) to 6 a.m. |
| South Carolina | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. during the summer break of the school district in which the minor resides) to 7 a.m. |
| South Dakota | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 4 hours per day and 20 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work after 10 p.m. prior to the school day. |
| Tennessee | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. to 7 a.m. (9 p.m. to 6 a.m. before non-school days); 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 10 p.m. to 6 a.m. (Sunday to Thursday prior to the school days; midnight with parental consent up to 3 nights a week). |
| Texas | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 10 p.m. (midnight before non-school day or in summer if not enrolled in summer school) to 5 a.m. |
| Utah | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 4 hours per day during school period. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 9:30 p.m. to 5 a.m. prior to the school day. |
| Vermont | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. |
| Virginia | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. |
| Washington | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 16 hours per week during school period. Up to 8 hours per day on Saturday and Sunday. Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 4 hours per day and 20 hours per week during school period. Up to 8 hours per day on Friday, Saturday, and Sunday. Up to 6 hours per day and 28 hours per week with parental, employer, student, and school consent. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. from June 1st to Labor Day) to 7 a.m. All minors working in service occupations after 8 p.m. must be supervised by an adult. 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 10 p.m. Sunday to Thursday (midnight Friday and Saturday when school isn’t in session) to 7 a.m. (5 a.m. when school isn’t in session); 9 p.m. to 7 a.m. in door-to-door sales. All minors working after 8 p.m. in service occupations must be supervised by an adult. |
| West Virginia | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. During the non-school day/week, 14 and 15-year-old minors are allowed to work until 11:00 p.m. with a supervision permit. |
| Wisconsin | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period. Up to 6 days per week. | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. |
| Wyoming | N/A | N/A | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 10 p.m. (midnight before non-school day and for minors not enrolled in school) to 5 a.m. |
Inhabited US territories also have their own regulations when it comes to youth employment.
| US territories | Maximum number of work hours and days for minors under 16 | Maximum number of work hours and days for minors aged 16 and 17 | Nightwork |
|---|---|---|---|
| District of Columbia | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week. Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 8 hours per day and 48 hours per week. Up to 6 days per week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. June 1 through Labor Day) to 7 a.m. 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 10 p.m. to 6 a.m. |
| Guam | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period (work and school hours combined. Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during school period (work and school combined). Up to 6 days per week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 7 p.m. (9 p.m. from June 1st through Labor Day) to 7 a.m.; 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 10 p.m. (midnight on non-school nights) to 6 a.m. |
| Puerto Rico | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during non-school period. Up to 8 hours per day during school period (work and school hours combined). Up to 6 days per week. | Up to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week. Up to 6 days per week. | Minors younger than 16 can’t work from 6 p.m. to 8 a.m. 16- and 17-year-old minors can’t work from 10 p.m. to 6 a.m. |
Frequently asked questions about the minimum working age
To make this guide as comprehensive as possible, we’ve added a section that includes a series of commonly asked questions about child labor.
What state has the youngest working age?
The state of Illinois has the youngest working age. Namely, Illinois child labor law allows 12-year-olds to work in agricultural jobs during school hours, while minors who wish to work outside school hours must be at least 10 years old.
According to child labor laws in Nevada and North Dakota, minors have to be at least 14 years old to work during school hours in agricultural jobs.
Other states that allow 14-year-olds to work in agriculture during school hours with labor certification are Vermont, Massachusetts, and New Mexico (hardship cases only). Circumstances that may cause someone to suffer undue hardship may include the following events:
- Extreme financial burden due to imminent foreclosure, eviction from home, loss of property or income,
- A medical condition resulting from an illness or accident,
- Funeral expenses, or
- A similar unforeseeable event that is beyond the control of the individual.
Moreover, in Oregon, the minimum age requirement outside school hours is 9, if the minor is involved in picking berries or beans (of course, with parental consent).
Want to learn more about North Dakota and Nevada labor laws? Everything you need to know is right here: North Dakota Labor Laws | Nevada Labor Laws
Can 12-year-olds get a job in the US?
The simple answer is yes, but there are a few limitations. Usually, 12-year-old minors can’t work in most non-agricultural jobs. However, there are still some non-agricultural work opportunities that are available for minors aged 12 and under, such as:
- Lawn mowing,
- Dog walking,
- Car washing,
- Window washing,
- Pool skimming,
- Fence painting, or
- Housekeeping.
According to the aforementioned FLSA regulations, the only exception is when the minor’s parents own the company. In such cases, minors of any age are legally authorized to work, but only in the above-mentioned non-hazardous jobs.
On the other hand, agricultural jobs offer more flexibility. Basically, 12-year-old minors can work in agricultural employment as long as they perform the work:
- Outside of school hours,
- Under non-hazardous work conditions, and
- With parental consent (for some states).
Here’s a list of states that allow 12-year-old minors to work in agriculture:
- California,
- Colorado,
- Illinois,
- Indiana,
- Iowa (in migratory labor),
- Minnesota,
- New Hampshire,
- New Jersey,
- New York (in hand-harvesting berries, fruits, and vegetables),
- Oregon,
- South Carolina (with parental consent),
- Utah,
- Virginia (with parental consent),
- Washington (in hand-harvesting berries, bulbs, cucumbers, and spinach), and
- Wisconsin.
Since employment rules for minors vary by state, make sure you check the limitations that might apply.
Can 14-year-olds work in the US?
Most US states allow 14-year-old minors to work in agricultural jobs outside of school hours. In fact, there are 15 states that follow a minimum working age of 14 (outside of school hours):
- Alaska,
- Arizona,
- Arkansas,
- Connecticut,
- Florida,
- Hawaii,
- Iowa,
- Maine,
- Massachusetts,
- Missouri,
- New York,
- Ohio,
- South Carolina,
- Virginia, and
- Washington.
The states that allow 14-year-old minors to perform work during school hours are the following:
- Massachusetts (with labor certification),
- Nevada,
- New Mexico (hardship cases only),
- North Dakota, and
- Vermont (with labor certification).
But, even though you can legally work at 14, federal laws (such as the FLSA) are strict about the working hours and the type of job you’re allowed to work. Additionally, before starting work in some states, 14-year-olds may need to submit relevant documents, such as:
- Proof of age,
- Employment certificate, or
- Parental approval.
Which states have a minimum working age under 14?
Although most states impose a minimum legal working age of 14, some exceptions exist. For example, Georgia child labor laws have set the minimum working age at 12. However, these rules apply only to employers not covered by the FLSA.
Under Georgia state labor laws, several types of jobs are approved for minors younger than 14, including:
- Babysitting,
- Newspaper delivery,
- Yard work,
- Shoe-shining,
- Entertainment jobs (acting, singing, or dancing), and
- Family business or family farm.
Furthermore, Georgia state laws require an employment certificate (or a work permit which the school provides) for minors under 18 before beginning work, while proof of age isn’t required.
Nevertheless, like many other US states, Georgia follows federal rules regarding hazardous occupations. Minors, regardless of age, can’t be employed in jobs that are deemed risky to their health and well-being.
Which states have a minimum working age of 16?
A few states allow 16-year-old minors (and beyond) to work in agricultural jobs during school hours.
The states that have set a minimum working age of 16 during school hours are:
- Alaska,
- Arizona,
- Arkansas,
- Colorado,
- Connecticut,
- Idaho,
- Iowa,
- Maine,
- Michigan,
- Minnesota,
- Missouri,
- New Jersey,
- New Mexico,
- New York,
- Ohio,
- Oregon,
- South Carolina,
- Utah,
- Vermont, and
- Virginia.
The FLSA has set employment restrictions on minors under 16 years of age, stating that work must be performed outside of school hours.
Schedule employee working hours with Clockify
Proper employee scheduling can benefit every business, as it ensures that employees aren’t overworked or underworked.
This can be especially useful if you’re employing minors, as there are limits on how many hours minors are allowed to work.
To be able to track work hours accordingly, you can use a time tracking software such as Clockify. With Clockify’s scheduling feature, you can easily schedule employee shifts and work hours, ensuring that no one is overworked or underworked.
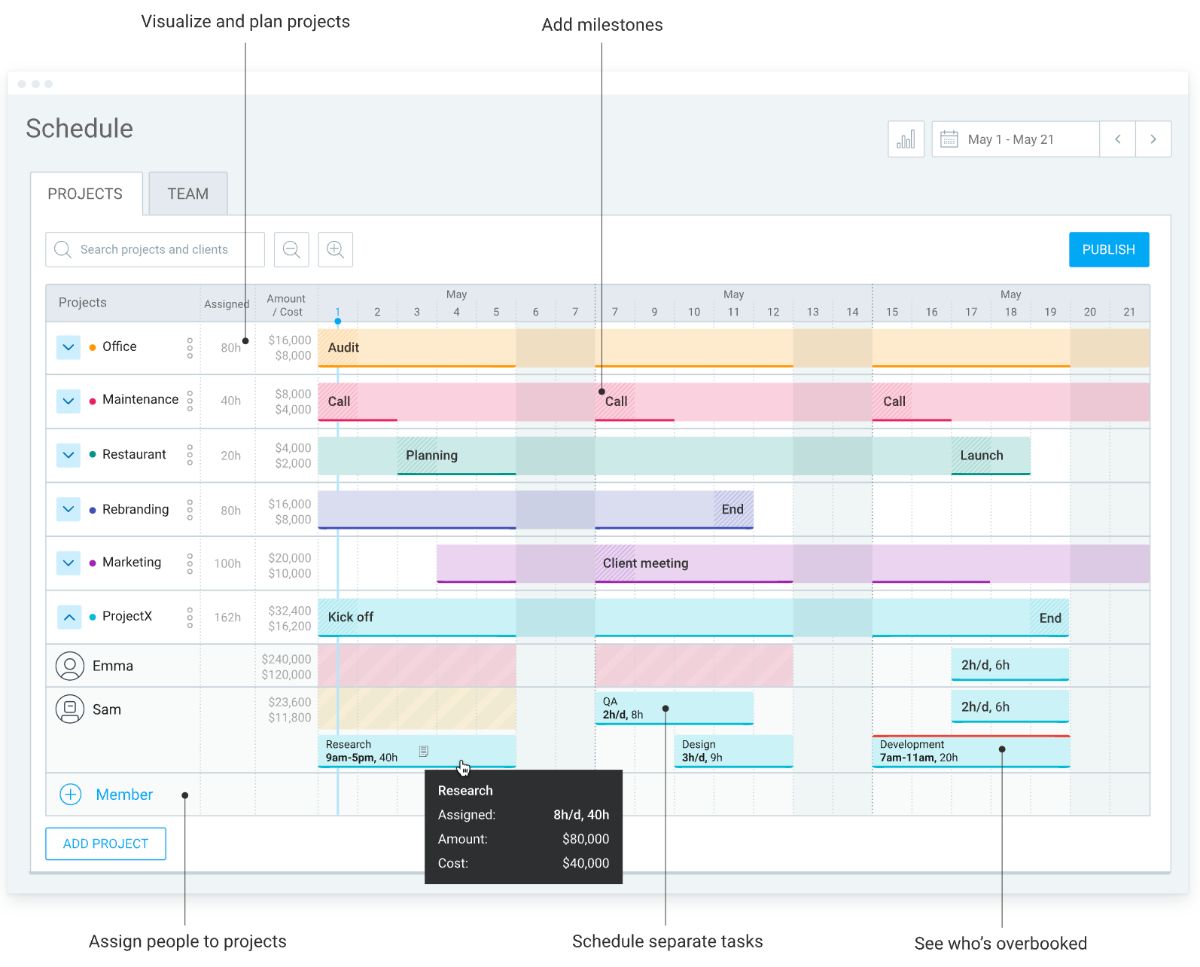
You can easily visualize and plan projects, add milestones, assign people to projects, and schedule separate tasks for every employee.
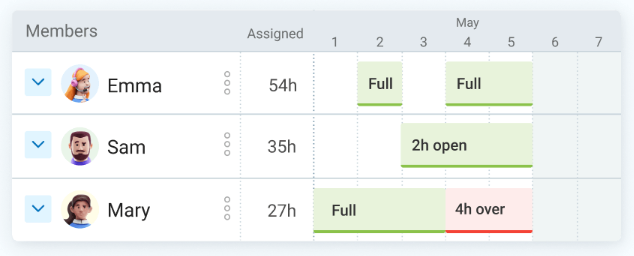
Once your projects are set, you can see how many working hours each employee has for that particular week. If an employee’s working hours are red, the employee is working overtime.
Clockify is simple, efficient, and reliable! Everything you need from time tracking software.
Conclusion/Disclaimer
We hope this paid minimum working age by state guide will be helpful. Please pay attention to the links provided, which will lead you to the official government websites and other relevant information.
Please note that this guide was written in February 2025, so any changes in the laws that were included later may not be in this guide.
We strongly advise you to consult with the appropriate institutions or certified representatives before acting on legal matters.
Clockify isn’t responsible for any losses or risks incurred should this guide be used without further guidance from legal or tax advisors.
How we reviewed this post: Our writers & editors monitor the posts and update them when new information becomes available, to keep them fresh and relevant. Updated: February 11, 2025
Updated: February 11, 2025